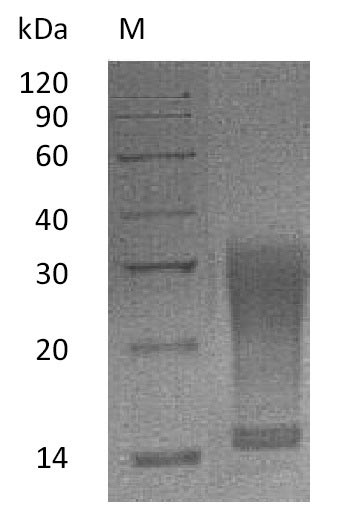
Recombinant Mouse Interleukin-13 (Il13) is expressed in a mammalian cell system and features a C-terminal 6xHis-tag for ease of purification. The protein represents a partial sequence spanning amino acids 26-131 and shows purity greater than 95% as verified by SDS-PAGE analysis. Biological activity appears robust, with an ED50 of 2-13 ng/ml in cell proliferation assays using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg, as determined by the LAL method.
Interleukin-13 is a cytokine that plays a role in immune regulation and inflammation. T-helper type 2 cells primarily produce this protein, and it influences various cell types. This likely contributes to the pathophysiology of allergic responses and asthma. The protein serves as an important component for studying immune responses and understanding regulatory mechanisms in inflammatory processes.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays
This recombinant mouse IL-13 is confirmed to be biologically active (ED₅₀ 2-13 ng/ml in human TF-1 cells) and suitable for proliferation studies. However, the partial sequence (26-131aa) and C-terminal His-tag may affect potency compared to full-length native IL-13. While mammalian expression ensures proper folding and glycosylation, researchers should validate activity in mouse-specific cell types (e.g., primary mouse B cells or airway epithelial cells) to confirm physiological relevance, as the activity data comes from human cells and may not reflect mouse-specific receptor affinity.
2. Cytokine Signaling Pathway Studies
The protein is appropriate for signaling studies, but the C-terminal His-tag may sterically affect receptor dimerization or signaling complex formation. The mammalian glycosylation supports authentic interactions, but researchers should validate that STAT6 phosphorylation kinetics and amplitude match those induced by tag-free IL-13. The partial sequence may lack domains important for some signaling functions, particularly regarding receptor binding kinetics.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
This mammalian-expressed IL-13 serves as a good antigen, but the C-terminal His-tag may induce tag-specific antibodies, reducing antibodies against native C-terminal epitopes. The partial sequence (lacking the N-terminal region) will generate antibodies with limited epitope coverage. Comprehensive validation should include testing against full-length, tag-free IL-13 to ensure recognition of all functional domains.
4. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The His-tag facilitates pull-down assays but may cause steric hindrance for C-terminal interactions or increase non-specific binding. While useful for initial screens, identified interactions should be validated with full-length, tag-free IL-13. The partial sequence may miss interactions dependent on the missing N-terminal region (aa 1-25). Low endotoxin minimizes false positives, but stringent controls are needed.
5. Comparative Species and Cross-Reactivity Studies
The demonstrated human cell activity enables cross-species comparisons, but the partial sequence and tag may confound direct functional comparisons with full-length human IL-13. The glycosylation pattern from mammalian expression supports authentic comparisons, but researchers should perform parallel assays with similarly tagged human IL-13 to eliminate tag-related variables when interpreting species differences.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This mammalian-expressed partial mouse IL-13 with a C-terminal His-tag is a functional reagent with confirmed cross-species bioactivity, but its truncated nature and tag require specific validation steps. For immediate use: 1) Employ it in the 2-20 ng/ml range based on the ED₅₀, but establish dose-response curves in mouse primary cells relevant to IL-13 biology (e.g., B cells, goblet cells); 2) For signaling studies, the mammalian glycosylation ensures proper folding, but validate early signaling events (STAT6 phosphorylation within 15-30 minutes) against tag-free IL-13 to detect potential tag-related kinetic differences; 3) When developing antibodies, use this protein for immunization but screen clones against full-length, tag-free IL-13 to ensure comprehensive epitope coverage; 4) For interaction studies, the tag is useful for purification but may require cleavage for precise binding measurements; 5) In comparative studies, include both mouse and human IL-13 proteins with identical tags and expression systems to control for technical variables. Always include appropriate controls (e.g., tag-only, unstimulated cells) and consider that different cell types may exhibit varying sensitivity to IL-13 stimulation based on receptor subunit expression (IL-13Rα1 vs IL-13Rα2). The mammalian expression ensures proper glycosylation, which is important for IL-13's stability and function, but the partial sequence and tag may affect some biological functions.