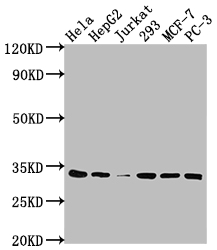
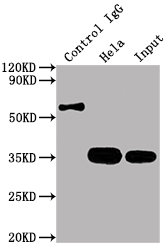
The CDK4 recombinant monoclonal antibody is yielded using protein and DNA recombinant technology. Initially, mice are immunized with a synthetic peptide derived from human CDK4. After a specific duration, spleen cells are isolated aseptically from the immunized mice, and the total RNA of the cells is extracted. cDNA, synthesized by RNA reverse transcription, serves as a template for PCR amplification of the CDK4 antibody gene. Subsequently, the gene is cloned into a vector and then transfected into host cells for culturing. The supernatant from the cultured cells is purified via affinity chromatography, resulting in the purified CDK4 recombinant monoclonal antibody. This antibody is extensively validated and can be employed in ELISA, WB, and IP experiments for the detection of human CDK4 protein.
The CDK4 protein is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a crucial role in regulating the progression of the cell cycle. CDK4 is one of the key components of the Cyclin D-CDK4/6 complex, which is involved in the G1/S transition of the cell cycle. The complex phosphorylates and inactivates the retinoblastoma protein (pRb), leading to the activation of E2F transcription factors and the transcription of genes required for DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. CDK4 is also involved in other cellular processes, such as differentiation, apoptosis, and transcriptional regulation, through its interactions with other proteins and signaling pathways. Dysregulation of CDK4 activity is implicated in many types of cancer.