What is an Fc gamma R?
First, we have to understand what is an Fc receptor. Fc receptor (FcR), short for fragment crystallizable receptor, is a receptor with an ability of specific binding for the tail region of an antibody known as the Fc region. The antibody is also called immunoglobulin (Ig). Fc gamma R (FcγR), a member of FcRs, can combine with the Fc fragment of IgG.
FcγRs belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily and play an important role in inducing phagocytosis of opsonized microbes. FcγRs comprise FcγRI (CD64), FcγRIIA (CD32a), FcγRIIB (CD32b), FcγRIIIA (CD16a), FcγRIIIB (CD16b). Their different molecular structure confers them various affinities to antibodies. Among them, FcγRI binds to IgG more strongly than other ones. Except for FcγRI, all FcγRs must bind to IgG-bound targets or the polymeric immune complexes to trigger receptor crosslinks and subsequent cellular responses. Because FcγRI has an extra Ig-like domain (D3), so it can bind to a monomer IgG.
What is Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis?
When an Fc gamma receptor on monocyte-macrophages or neutrophils combines with the IgG via its Fc region, it causes phagocytosis. This process is called Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis.
The Function of Fc gamma R-mediated Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a necessary component of the innate immune response. And phagocytosis plays a crucial role in host-defense mechanisms by uptaking and destructing infectious pathogens. In infectious condition, the Fc gamma R-mediated Phagocytosis opsonizes and clears pathogen particles or microbes. The interaction between Fc-FcγR mediates intracellular protective activity against monoclonal antibody (mAb). Besides, the involvement of the Fc gamma R of the immune complex induces multipotent pro-inflammatory and immunomodulatory functions and is potential to trigger a sustained antimicrobial immune response.
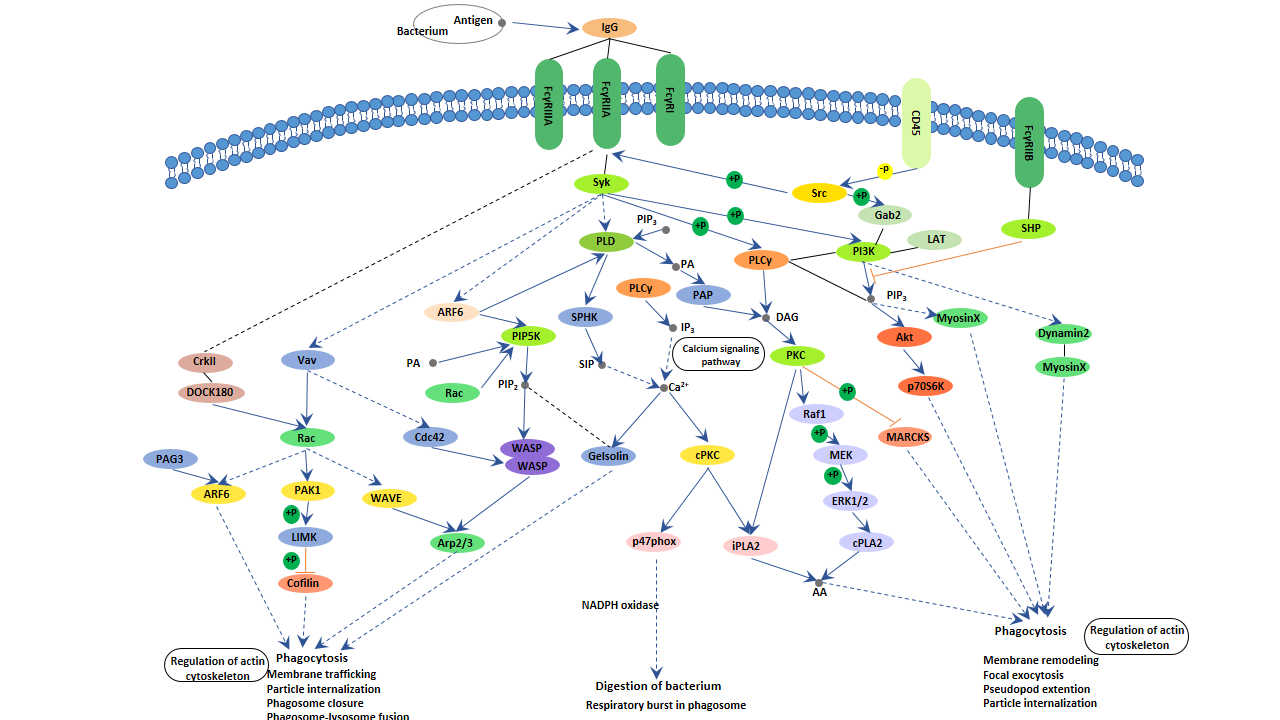
The Mechanism of Fc gamma R-mediated Phagocytosis
Fc gamma receptor is an essential participant in many immune system effector functions such as phagocytosis of opsonized, release of inflammatory mediators and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Here, we primarily illustrate the mechanism of Fc gamma R mediated phagocytosis.
Upon crosslinking by Immune complexes (IgG-antigen complexes or microbes coated with IgGs), Fc gamma receptors generate signals within their cytoplasmic domain through an important activation motif, ITAM (Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif). Phagocytosis is triggered by clustering of FcγRs. At the sites of clustering of FcγRs, the immune cells (macrophages, neutrophils, and monocytes) contact with the opsonized particles and starts with tyrosine phosphorylation of the ITAMs in the cytoplasmic domains of these receptors by kinases of the SRC family. This leads to the recruitment of SYK-family kinases, followed by the activation of various downstream targets such as the linker for activation of T cells (LAT), multimolecular adaptor complexes, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (P13K). And then, PI3K activates phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ). Activation of PLCγ causes an increased intracellular calcium level and triggers the calcium signaling pathway. Besides, cross-linking of Fc gamma receptors initiates a variety of signals mediated by tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple proteins, which results in the actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and membrane remodeling to form phagosomes. Nascent phagosomes undergo a process of maturation that involves fusion with lysosomes. The acquisition of lysosomal proteases and release of reactive oxygen species are crucial for digestion of engulfed materials in phagosomes.
The Applications of Fc gamma R-mediated Phagocytosis
Considered to the modulating functions of phagocytosis mediated by Fc gamma Rs in the immune response, it shows great potential to the development of new immunotherapeutic avenues.
FcγRs play an important role in determining the therapeutic activity of monoclonal IgG antibodies (mAbs). Because they can activate the cytotoxic activity of FcγR-positive cells such as NK cells, monocytes, macrophages & neutrophils and increase antigen presentation through DC when ligated by the Fc portion of therapeutic antibodies. Recent studies in Fc receptor-deficient nude mice show that the anti-tumor effects of mAbs such as those directed at-CD20 and HER2 that requires the presence of the signal-transducing Fcγ chain. And the signal-transducing Fcγ chain involves in the activation of FcγRI and FcγRIII receptors expressed on monocytes, macrophages, and NK cells.
Previous studies have proved that Phagocytosis via Fc-Gamma Receptors is compromised in monocytes from Type II Diabetes patients with chronic hyperglycemia. It may provide a strategy to treat patients with Type II Diabetes companied chronic hyperglycemia.





