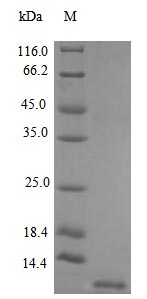
Recombinant Human Stromal cell-derived factor 1 protein (CXCL12) is produced in an E. coli expression system and represents a partial sequence spanning amino acids 22 to 89. This tag-free protein achieves a purity level exceeding 97%, as confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis. It appears to be fully biologically active, with activity validated via a chemotaxis bioassay using activated human peripheral blood T-lymphocytes, effective at concentrations between 20-80 ng/ml. The endotoxin level remains below 1.0 EU/µg, as determined by the LAL method.
CXCL12, also known as Stromal cell-derived factor 1, plays what seems to be a crucial role in cellular signaling. This chemokine functions primarily in the immune system, directing the movement and localization of cells through chemotaxis. CXCL12 is integral to processes such as hematopoiesis and organ development, which makes it a significant focus in research related to cell migration and immune response pathways.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. T-lymphocyte Chemotaxis Assays
This recombinant CXCL12 protein is confirmed to be biologically active in chemotaxis assays using activated human T-lymphocytes (active at 20-80 ng/ml) and suitable for studying T-cell migration. The high purity (>97%) and low endotoxin levels ensure minimal interference in cell-based migration experiments. However, researchers should note that the optimal concentration may vary for different T-cell subsets or activation states, and dose-response optimization is recommended for specific experimental conditions.
2. CXCR4 Receptor Binding Studies
The biologically active CXCL12 is appropriate for studying CXCR4 interactions, but the provided concentration range (20-80 ng/ml) is for functional chemotaxis, not direct binding measurements. For binding studies (SPR, competitive binding), researchers should empirically determine the appropriate concentration range, as binding affinity (Kd) may be different from functional EC₅₀ values. The confirmed bioactivity indicates proper folding for receptor engagement.
3. Cell Signaling Pathway Analysis
This CXCL12 protein can be used to investigate downstream signaling cascades (e.g., MAPK, PI3K pathways) through CXCR4 activation. The low endotoxin content ensures specific attribution of signaling responses to CXCL12. However, researchers should validate signaling kinetics in their specific cell models, as the provided activity range was established in activated T-lymphocytes and may not directly translate to signaling amplitude or timing in other cell types.
4. Antibody Development and Validation
The high-purity, full-length mature CXCL12 (22-89aa, isoform alpha) serves as an excellent antigen for antibody development. The confirmed biological activity ensures proper folding for conformational epitope presentation. However, since CXCL12 has multiple isoforms (alpha, beta, gamma, etc.), antibodies generated against this alpha isoform should be tested for cross-reactivity with other isoforms if pan-CXCL12 detection is desired.
5. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The biologically active, tag-free CXCL12 is suitable for studying interactions beyond CXCR4, including with ACKR3 (CXCR7) or glycosaminoglycans. However, researchers should note that the E. coli expression system lacks natural post-translational modifications (e.g., O-glycosylation at Serine 5 in native CXCL12) that might affect some interactions. Critical findings should be validated with mammalian-expressed CXCL12 when studying modification-sensitive interactions.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed human CXCL12 (SDF-1α) is a well-validated reagent suitable for all proposed applications, with confirmed biological activity in T-lymphocyte chemotaxis assays. For immediate use, employ it within the 20-80 ng/ml range for migration studies, but perform dose-response optimization for specific cell types and experimental conditions. For receptor binding studies, determine appropriate concentrations empirically rather than relying solely on the functional chemotaxis data. When developing antibodies, this protein is ideal for generating isoform-specific reagents, but test cross-reactivity with other CXCL12 isoforms if broad specificity is required. While the E. coli expression produces a non-glycosylated form, the demonstrated bioactivity confirms proper folding for core CXCL12 functions, though researchers should validate key findings with mammalian-expressed protein when studying modification-dependent interactions. Always include proper controls and consider that different cell types may exhibit varying sensitivity to CXCL12 stimulation.