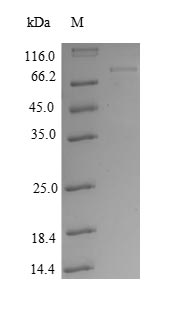
To produce recombinant human AKT1 in E. coli, the gene of interest is co-cloned into a vector with an N-terminal GST-tag gene and transformed into E. coli cells. The gene of interest encodes the full-length human AKT1 (1-480aa). The cells are cultured to express the AKT1 protein and then lysed to extract it. The harvested protein is purified using affinity chromatography. Its purity is checked with SDS-PAGE, reaching over 90%.
The Human AKT1 protein is a serine/threonine-protein kinase that belongs to the protein kinase B (PKB) family. AKT1 phosphorylates various substrates, indicating its role in diverse cellular processes [1]. It plays a crucial role in various cellular processes such as cell growth, survival, glucose metabolism, genome stability, and neovascularization [2][3]. The phosphorylation-dependent substrate selectivity of AKT1 underscores its specificity in signaling cascades [4]. AKT1 is a key mediator of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, which is essential for regulating cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis, particularly in cancer [5]. Human AKT1 has been identified to have 215 unique human proteins as its experimentally verified substrates, highlighting its significance in cellular signaling networks [6]. The activation of AKT1 is initiated by binding its pleckstrin homology (PH) domain to phosphoinositides, followed by phosphorylation at specific regulatory amino acids, serine 473 and threonine 308 [7].
References:
[1] M. McKenna, N. Balasuriya, S. Zhong, S. Li, & P. O’Donoghue, Phospho-form specific substrates of protein kinase b (akt1), Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, vol. 8, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.619252
[2] Y. Yoshioka, T. Suzuki, Y. Matsuo, M. Nakakido, G. Tsurita, C. Simoneet al., Smyd3-mediated lysine methylation in the ph domain is critical for activation of akt1, Oncotarget, vol. 7, no. 46, p. 75023-75037, 2016. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11898
[3] J. Testa and A. Bellacosa, Akt plays a central role in tumorigenesis, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 98, no. 20, p. 10983-10985, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.211430998
[4] N. Balasuriya, N. Davey, J. Johnson, H. Liu, K. Biggar, L. Cantleyet al., Phosphorylation-dependent substrate selectivity of protein kinase b (akt1), Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 295, no. 24, p. 8120-8134, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra119.012425
[5] H. Zhao, B. Martin, M. Bisoffi, & D. Dunaway-Mariano, The akt c-terminal modulator protein is an acyl-coa thioesterase of the hotdog-fold family, Biochemistry, vol. 48, no. 24, p. 5507-5509, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi900710w
[6] F. Chen, Q. Liu, T. Hilliard, T. Wang, H. Liang, W. Gaoet al., A chemical-genetics and nanoparticle enabled approach for in vivo protein kinase analysis,, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.13.094573
[7] A. Kumar, V. Rajendran, R. Sethumadhavan, & R. Purohit, Akt kinase pathway: a leading target in cancer research, The Scientific World Journal, vol. 2013, p. 1-6, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/756134