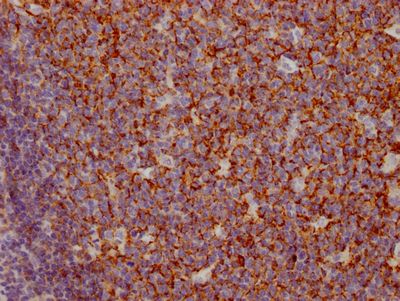
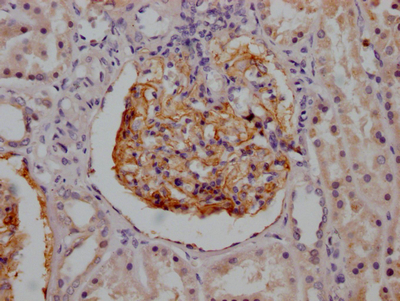
The preparation of a CR1 recombinant monoclonal antibody involves four steps: sequencing the gene that codes for the CR1 monoclonal antibody, cloning the gene into a plasmid vector, introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell line, and purifying the CR1 recombinant monoclonal antibody using affinity chromatography. To produce the CR1 monoclonal antibody, a synthesized peptide derived from human CR1 is used as the immunogen. This CR1 recombinant monoclonal antibody has been recommended for detecting human CR1 protein in ELISA and IHC applications.
The CR1 protein, also known as CD35, plays an important role in the regulation of the complement system, a part of the immune system that helps to destroy foreign particles such as bacteria and viruses. CD35 acts as a cofactor for the cleavage of complement components C3b and C4b, which are then degraded by other complement proteins, preventing the formation of large immune complexes and the activation of inflammatory pathways thus causing tissue damage. Additionally, CD35 has been shown to be involved in the clearance of apoptotic cells, immune complexes, and other debris from the bloodstream.