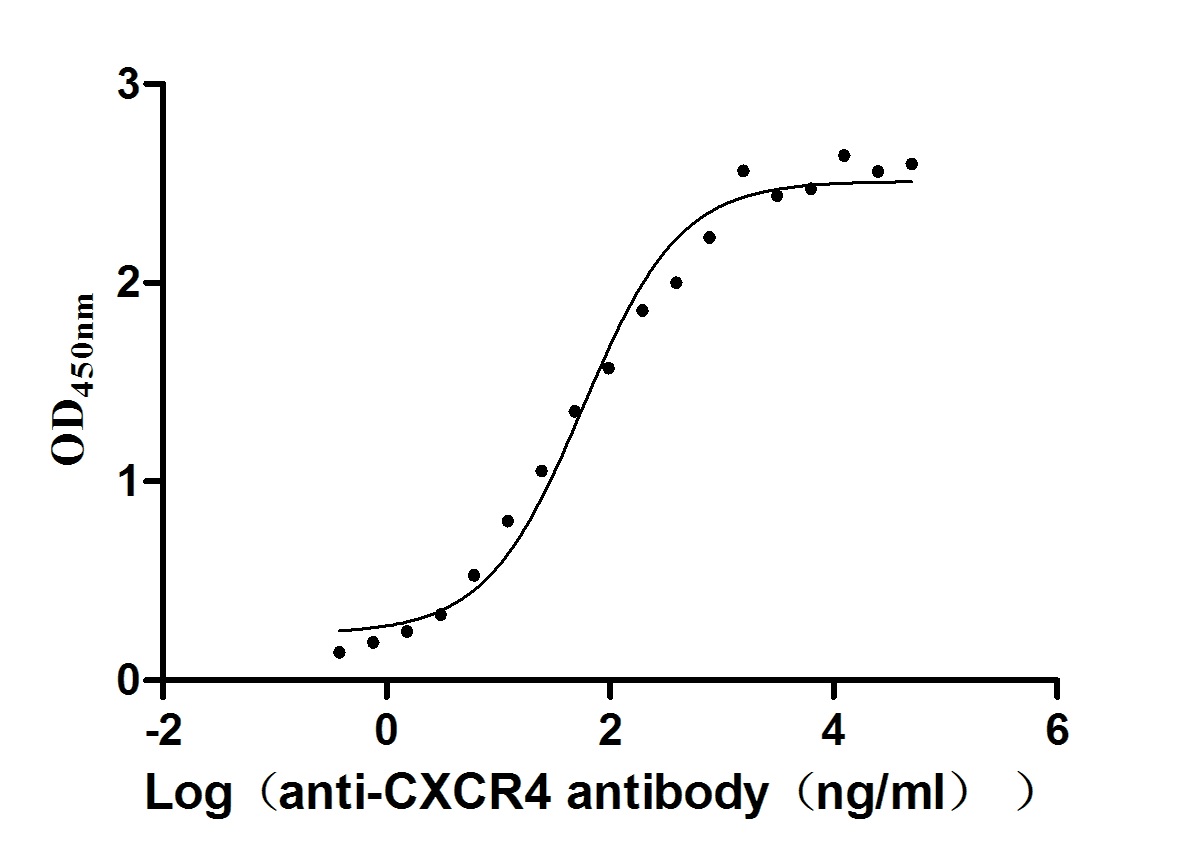
The recombinant human CXCR4 protein is produced through gene cloning, plasmid construction, protein expression, purification, and analysis. The human CXCR4 gene (1-352aa) is co-inserted into a lentiviral vector with a C-terminal 10xHis-tag gene. The recombinant lentiviral vector is transfected into mammalian cells, and after 24 hours, a selective antibiotic is introduced to isolate transfected cells. The transfected cells are cultured to express the CXCR4 protein. After that, the viral capsid proteins are added to the medium to induce the formation of virus-like particles (VLPs). The VLPs are isolated and purified from the medium through ultracentrifugation or affinity chromatography. Their biological activity is validated through a functional ELISA, in which this human CXCR4 protein binds to the CXCR4 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA006254MA01HU), with an EC50 of 101.7-253.6 ng/mL.
The human CXCR4 protein, a member of the GPCR family, primarily functions as a receptor for the chemokine CXCL12 (SDF-1), which is crucial for the migration and homing of hematopoietic stem cells, lymphocytes, and other immune cells [1]. The interaction between CXCR4 and CXCL12 is essential for normal development, immune response, tissue repair, and the progression of several diseases, including cancer and HIV infection [2][3].
CXCR4 is expressed in a wide variety of tissues, including the brain, bone marrow, and lymphoid organs. Its expression levels can vary significantly depending on the cellular context and the presence of specific stimuli [1]. CXCR4 is often overexpressed in tumor cells and is associated with increased metastasis and poor prognosis in various cancers such as breast, lung, and colorectal cancers [3]. It is involved in tumor cell migration, invasion, and the establishment of metastatic niches [4]. Moreover, CXCR4 serves as a co-receptor for HIV-1, facilitating viral entry into host cells [2][3].
β-arrestins play a critical role in regulating CXCR4 signaling, receptor internalization, and desensitization, which are vital for maintaining cellular responses to chemokines [5][6]. Additionally, CXCR4 undergoes post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, which modulate its activity and interactions with other proteins [7]. It can also form heteromers with other GPCRs, such as α1-adrenergic receptors, influencing its signaling dynamics and functional outcomes [8][9].
References:
[1] J. Lao, H. He, X. Wang, Z. Wang, Y. Song, B. Yang, et al. Single-molecule imaging demonstrates ligand regulation of the oligomeric status of cxcr4 in living cells, The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 121, no. 7, p. 1466-1474, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b10969
[2] M. Triantafilou, P. Lepper, C. Briault, M. Ahmed, J. Dmochowski, C. Schümann, et al. Chemokine receptor 4 (cxcr4) is part of the lipopolysaccharide “sensing apparatus”, European Journal of Immunology, vol. 38, no. 1, p. 192-203, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200636821
[3] E. Smith, R. Ogert, D. Pechter, A. Villafania, S. Abbondanzo, K. Lin, et al. Hiv cell fusion assay: phenotypic screening tool for the identification of hiv entry inhibitors via cxcr4, Slas Discovery, vol. 19, no. 1, p. 108-118, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057113500074
[4] F. Tanios, J. Pelisek, B. Lutz, B. Reutersberg, E. Matevossian, K. Schwamborn, et al. Cxcr4: a potential marker for inflammatory activity in abdominal aortic aneurysm wall, European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, vol. 50, no. 6, p. 745-753, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.07.040
[5] Z. Cheng, J. Zhao, Y. Sun, W. Hu, Y. Wu, B. Cen, et al. Β-arrestin differentially regulates the chemokine receptor cxcr4-mediated signaling and receptor internalization, and this implicates multiple interaction sites between β-arrestin and cxcr4, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 275, no. 4, p. 2479-2485, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.4.2479
[6] J. Luo, J. Busillo, R. Stumm, & J. Benovic. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 3 and protein kinase c phosphorylate the distal c-terminal tail of the chemokine receptor cxcr4 and mediate recruitment ofβ-arrestin, Molecular Pharmacology, vol. 91, no. 6, p. 554-566, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.116.106468
[7] W. Mueller, D. Schütz, F. Nagel, S. Schulz, & R. Stumm. Hierarchical organization of multi-site phosphorylation at the cxcr4 c terminus, Plos One, vol. 8, no. 5, p. e64975, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064975
[8] T. Abhishek, P. Vana, T. Chavan, L. Brueggemann, K. Byron, N. Tarasova, et al. Heteromerization of chemokine (c-x-c motif) receptor 4 with α1a/b-adrenergic receptors controls α1-adrenergic receptor function, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 112, no. 13, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417564112
[9] X. Gao, L. Albee, B. Volkman, V. Gaponenko, & M. Majetschak. Asymmetrical ligand-induced cross-regulation of chemokine (c-x-c motif) receptor 4 by α1-adrenergic receptors at the heteromeric receptor complex, Scientific Reports, vol. 8, no. 1, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21096-4

-WB.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)