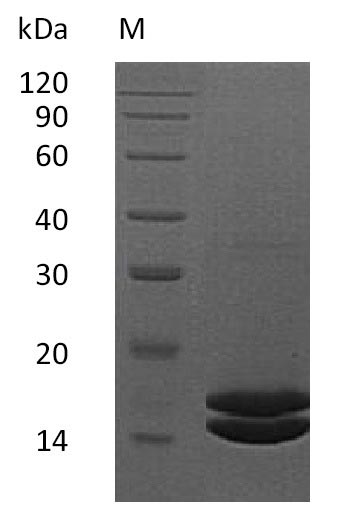
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) is expressed in a mammalian cell system and contains the full-length mature protein sequence from amino acids 21-153. The protein carries a C-terminal 6xHis tag and shows purity greater than 95% when analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Biological activity appears robust, with specific activity of ≥1×10^7 IU/mg demonstrated in CTLL-2 cell proliferation assays. Endotoxin levels stay below 1.0 EU/µg, as measured by the LAL method.
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) stands as one of the more important cytokines in immune system function. Its primary job involves driving T cell proliferation and differentiation, though its role extends beyond these basic functions. The protein seems central to immune response regulation and is particularly critical for activating and promoting growth in specific immune cell types. Given this fundamental importance, IL-2 has become a major research target in immunology, cell biology, and therapeutic development.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. T Cell Proliferation and Activation Studies
This recombinant human IL-2 is highly biologically active (≥1×10⁷ IU/mg in CTLL-2 cells) and suitable for T cell studies. However, the C-terminal His-tag may affect receptor binding kinetics as the C-terminus is involved in IL-2 receptor β chain interactions. While mammalian expression ensures proper folding and glycosylation, researchers should validate that proliferation kinetics and activation markers in human primary T cells match those induced by tag-free IL-2. The high specific activity confirms functionality, but optimal concentrations may need adjustment for different T cell subsets.
2. Cytokine Receptor Binding and Signaling Research
The biologically active IL-2 is appropriate for receptor studies, but the C-terminal His-tag may sterically hinder interactions with the IL-2 receptor complex (particularly IL-2Rβ and γc chains). While the tag facilitates detection, binding kinetics should be validated with tag-free IL-2 for accurate measurements. The mammalian glycosylation ensures native-like receptor engagement, but signaling amplitude and duration may be affected by the tag.
3. Immunological Assay Development and Standardization
This IL-2 serves as an excellent standard for assay development due to its high purity and defined activity. However, the His-tag may affect antibody recognition in immunoassays if antibodies target C-terminal epitopes. Assays should be validated against international standards or tag-free IL-2 to ensure accurate quantification. The mammalian expression ensures proper epitope presentation for most immunological applications.
4. Antibody Development and Characterization
The mammalian-expressed IL-2 is a good antigen, but the C-terminal His-tag may induce tag-specific antibodies, reducing antibodies against native C-terminal epitopes. Comprehensive validation should include testing against tag-free IL-2 to ensure recognition of physiological forms. The high specific activity supports the development of function-blocking antibodies.
5. Cell Culture Medium Supplementation for Research
The protein is suitable for cell culture, but the His-tag may affect long-term stability or induce immune responses in sensitive assays. For extended cultures (>72 hours), researchers should validate that T cell differentiation patterns (e.g., Treg vs effector cell expansion) match those induced by tag-free IL-2. The low endotoxin supports sensitive primary cell cultures.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This mammalian-expressed human IL-2 with a C-terminal His-tag is a high-quality reagent with excellent bioactivity, making it suitable for most proposed applications with appropriate validation for tag-related effects. For T cell studies, use concentrations based on the specific activity (typically 10-100 IU/ml, equivalent to ~1-10 ng/ml), but validate proliferation and activation kinetics in human primary T cells compared to tag-free IL-2. For receptor binding studies, the tag facilitates immobilization but may alter kinetics; consider tag cleavage for precise measurements. When developing immunoassays, this protein is ideal as a standard due to its defined activity, but it ensures antibodies recognize both tagged and native IL-2 forms. For antibody development, use this protein for immunization, but screen clones against tag-free IL-2 to avoid tag-dominated responses. For cell culture supplementation, the protein is effective for short-term studies, but for therapeutic T cell expansion or long-term cultures, validate that differentiation outcomes match tag-free IL-2. The mammalian expression ensures proper glycosylation, which is important for stability and function. Always include appropriate controls (e.g., tag-free IL-2 when available) and consider that different T cell subsets may have varying sensitivity to IL-2 stimulation.