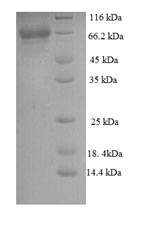
Recombinant Human Calpastatin (CAST) is expressed in E. coli and includes the complete sequence of isoform 4, spanning amino acids 1 to 667. An N-terminal 6xHis tag is attached to the protein, which simplifies purification and detection processes. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the product maintains purity levels exceeding 90%, making it well-suited for research applications that demand high-quality reagents.
Calpastatin functions as a specific inhibitor of calpain, a calcium-dependent cysteine protease. The protein appears to play a critical role in controlling calpain activity, which participates in various cellular processes—cytoskeletal remodeling and signal transduction pathways among them. Research into calpastatin's interactions and inhibitory mechanisms may prove essential for understanding cellular regulation and proteolytic balance.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant Human Calpastatin is expressed in E. coli, a prokaryotic system that may not support proper folding of this large, multi-domain eukaryotic protein (667aa). Calpastatin requires specific domain folding to function as a calpain inhibitor, with its activity dependent on conformational flexibility and domain accessibility. While E. coli can express soluble proteins, the complex domain structure of calpastatin (particularly its four inhibitory domains) may not fold correctly without eukaryotic chaperones. The N-terminal 6xHis tag could potentially interfere with N-terminal function. Since activity is unverified, the protein cannot be assumed to be correctly folded or bioactive without functional validation (e.g., calpain inhibition assays).
1. Calpain-Calpastatin Interaction Studies
This application is highly dependent on correct folding. If calpastatin is properly folded, it can be used to study interactions with calpain-1/2 through binding kinetics and inhibition assays. However, if misfolded, the inhibitory domains may not interact correctly with calpains, leading to inaccurate binding data. The His-tag facilitates immobilization for SPR, but results require validation with functional inhibition assays. It should emphasize that activity verification is a prerequisite for meaningful interaction studies.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is well-supported. The recombinant calpastatin can serve as an effective immunogen for antibody generation, as antibodies may recognize linear epitopes even if the protein is misfolded. The high purity (>85%) and full-length sequence ensure broad epitope coverage. However, antibodies may not recognize conformational epitopes of native calpastatin if folding is incorrect. Validation against endogenous calpastatin is recommended.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Screening
This application carries a significant risk without folding validation. While pull-down assays are technically feasible with the His-tag, misfolded calpastatin may exhibit non-physiological interactions, potentially identifying false binding partners. This application should only be pursued after confirming native folding and calpain inhibitory activity.
4. Biochemical Characterization Studies
This application is appropriate and should be prioritized. Techniques like circular dichroism spectroscopy can directly assess secondary structure and folding quality. Thermal stability and pH sensitivity studies provide valuable data on the protein's biophysical properties. These studies are useful even if the protein is inactive, as they characterize the recombinant product.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Given the uncertainty in folding and bioactivity, the recommended approach is to first perform biochemical characterization (Application #4) to assess the protein's folding state, followed by functional validation using calpain inhibition assays. If the protein demonstrates inhibitory activity against calpain-1/2, it can be reliably used for interaction studies (Applications #1 and #3). For antibody development (Application #2), the protein can be used immediately, but the resulting antibodies should be validated against native calpastatin. Always include appropriate controls, such as active calpain enzymes and known calpastatin standards in functional assays. The E. coli expression system may produce functional calpastatin, but verification is essential given the protein's complexity and functional dependence on correct domain folding.