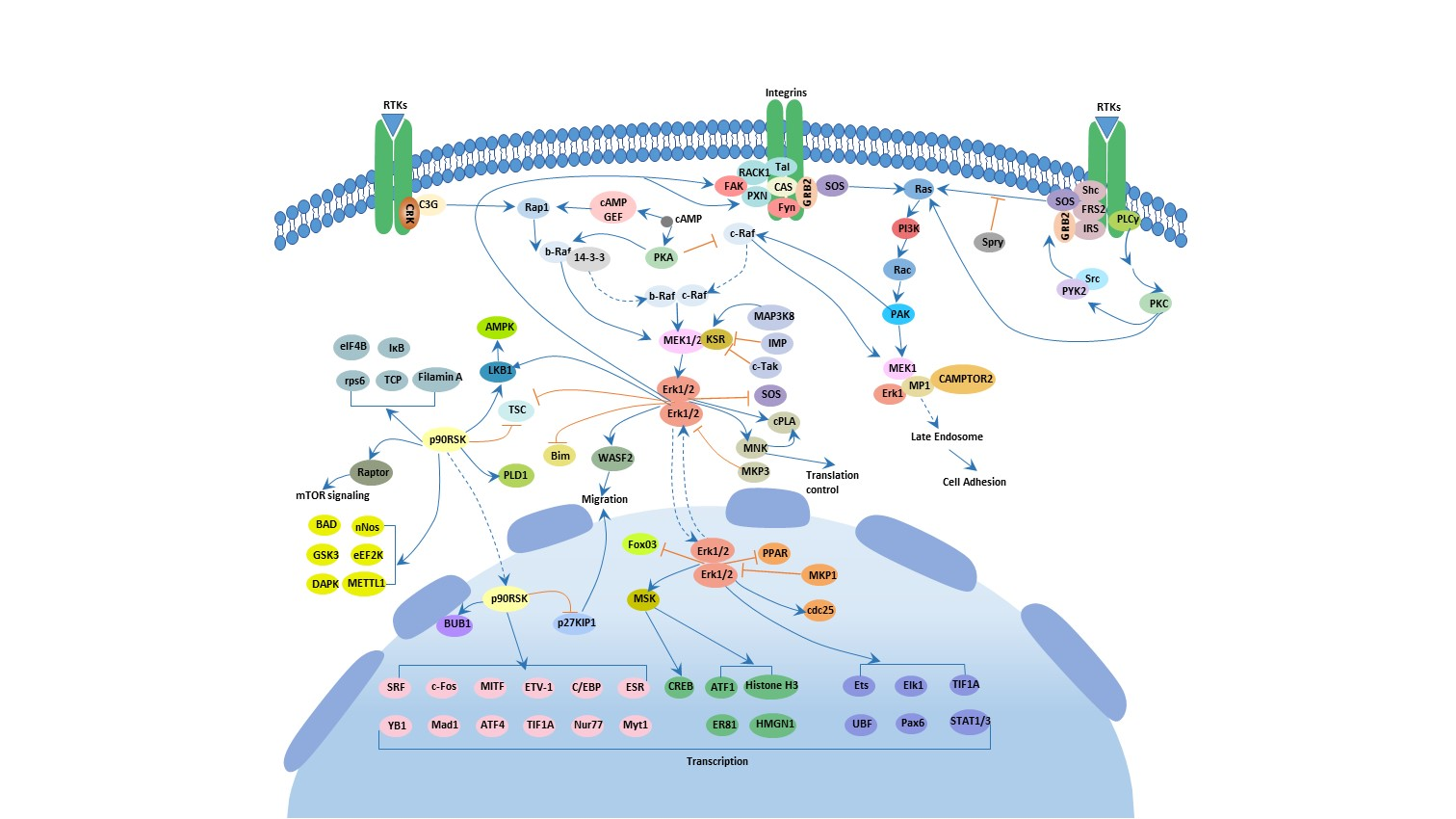
What is The MAPK-ERK Signaling Pathway?
MAPKs signaling pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway, which exists in lower prokaryotic cells and higher mammalian cells. The signaling pathway can transduce extracellular stimulation signals into cells and their nucleus, and ultimately cause a series of biological reactions such as cell proliferation, differentiation, transformation and apoptosis.
The Function of MAPK-ERK Signaling Pathway
MAPK-ERK signaling pathways also called Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, which is the main signal pathway of MAPK signal pathway. The major functions of this signaling pathway involve the regulation of cell proliferation, transformation, differentiation and apoptosis. This signaling pathway is activated by a variety of hormones, growth and differentiation factors, tumour-promoting substances.
The Process of MAPK-ERK Signaling Pathway
Receptor tyrosine kinases, G-protein-coupled receptors , and/or integrins activate small GTPases Ras (and possibly Rap) as the beginning of this signaling pathway. These membrane proteins recruit and activate Ras proteins by inducing exchange of Ras-bound GDP with GTP. And the inactivation of the Ras is controlled by GAPs (GTPase - activation proteins), which promote the hydrolysis of GDP by GTP by enhancing Ras GTPase activity. Upon activation, the small G protein recruits MKKKs c-Raf (A-Raf and B-Raf) onto the plasma membrane and activates it. Activated Raf activates MEK-1/2 by phosphorylating serine residues. MEK-1/2 activates ERK-1/2 by phosphorylating the threonine and tyrosine residues of ERK-1/2.
Activated ERK can phosphorylate some nuclear transcription factors such as c-fos, c-Jun, Elk-1, c-myc and ATF2, which are directly involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. It also targets indirect regulation of gene expression by substrates such as p90-RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase). In addition, ERK can also perform its own negative feedback regulation by phosphorylating upstream proteins of the ERKs pathway such as NGF receptor, SOS, Raf-1, MEK, and the like. Other studies have shown that ERKs phosphorylates cytoskeletal components in the cytoplasm, such as tubule-associated proteins MAP-1, MAP-2, and MAP-4, thereby participating in the regulation of cell morphology and the redistribution of cytoskeleton.
The MAPK-ERK Signaling Pathway and Cancer
Cancer occurs when the genetic and epigenetic alterations disturb the body's normal control mechanism. Many essential signaling cascades change in cancer, such as the MAPK-ERK pathway. The mutations in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK genes of the signaling pathway are found in the bulk of solid tumors. RAS mutants encode mutated proteins, which are GAP-insensitive and constitutively GTP-bound, leading to stimulus-independent and sustained activation of ERK1/2. Oncogenic BRAF mutations result in hyperactivation of its downstream effectors MEK and ERK1/2. Besides, aberrant activation of receptor tyrosine kinases has been reported in numerous human cancer. All of the upstream mutations can evoke ERK protein overactivation, which further phosphorylates and activates a series of ERK-signaling-regulated substrates such as CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein), c-Myc (transcriptional regulator Myc-like) and NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa B), AP-1, ETS-1, as well as members of the signal transducer and activator of transcription family. The functional consequences of substrate-level phosphorylation by ERK1/2 include changes in cellular motility and gene expression that promote proliferation, differentiation, migration, and angiogenesis of tumor cells. Overexpression of ERK1/2 also induces regulation of anti-apoptotic molecules such as BCL-2, thus inhibiting tumorous apoptosis. In terms of the close association between aberrant activation of the MAPK-ERK pathway and various kinds of cancers, manipulation of this pathway and its downstream molecules is a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment.





