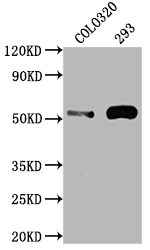
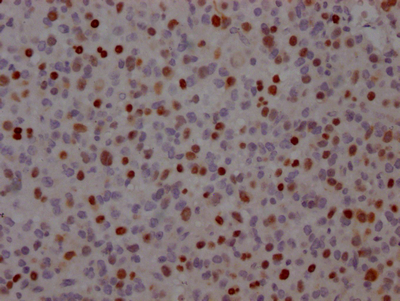
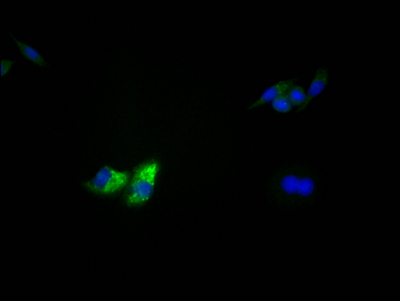
The TP53 recombinant monoclonal antibody can detect human TP53 protein in ELISA, WB, IHC, and IF applications. It is produced using recombinant DNA technology, where the gene encoding the TP53 monoclonal antibody is synthesized after sequencing the cDNA of the TP53 antibody-producing hybridomas. To produce the hybridomas, B cells isolated from an animal immunized with a synthesized peptide derived from human TP53 are fused with myeloma cells. The synthesized gene is then cloned into a vector and transfected into cells for cultivation. The resulting TP53 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified through affinity chromatography from the cell culture supernatant.
The TP53 protein, also known as p53, acts as a tumor suppressor by preventing cells from dividing when they have damaged DNA that could lead to the development of cancer. When DNA damage or other cellular stress occurs, the levels of p53 increase, which leads to the activation of multiple pathways that can result in several outcomes, including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence, and DNA repair. Mutations in TP53 that lead to loss of TP53 function can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and the development of tumors.