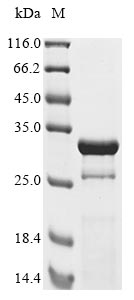
Constructing a plasmid that codes for the human adenovirus B serotype 3 (HAdV-3) Hexon protein (L3) (625-853aa) along with the N-terminal 10xHis-tag gene and C-terminal Myc-tag gene is the initial step to yield the recombinant HAdV-3 Hexon protein. The plasmid is then transferred into E.coli cells. Positive E.coli cells are selected and cultured for protein expression. CUSABIO uses affinity chromatography to purify the protein. The SDS-PAGE analysis is carried out to verify the presence and assess the purity of the protein. The protein possesses a purity exceeding 85%.
Hexon protein is a vital component of adenoviruses, serving as one of the major capsid proteins associated with different viral species or serotypes [1]. It is the most abundant capsid protein, with 240 hexon capsomers, each consisting of a trimer of hexon proteins [2]. Hexon forms a total of 240 trimers on the surface of the icosahedral capsid, making it the most abundant viral capsid protein [3]. The hexon capsomer is an oligomeric protein with three subunits, and its structure and function are influenced by genetic material from specific regions of the viral genome [4]. Furthermore, hexon plays a significant role in the natural liver tropism of adenoviruses [5].
Hexon proteins are essential for inducing the formation of group-specific antibodies and contain major serotype-specific B cell epitopes [6][7]. They are type-specific, and replacing one type of adenovirus hexon with another can alter the neutralizing antigenic properties [8]. The hexon protein is structurally complex, with multiple hypervariable regions containing serotype-specific residues [9]. It is also involved in interactions with scavenger receptors Khare et al. [5] and is crucial for adenovirus assembly, with its nuclear import mediated by protein VI [10].
References:
[1] J. Liu, N. Mei, Y. Wang, X. Shi, & H. Chen, Identification of a novel immunological epitope on hexon of fowl adenovirus serotype 4, Amb Express, vol. 11, no. 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-021-01309-2
[2] G. Singh, X. Zhou, Y. Lee, M. Yousuf, M. Ramke, A. Ismailet al., Recombination of the epsilon determinant and corneal tropism: human adenovirus species d types 15, 29, 56, and 69, Virology, vol. 485, p. 452-459, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2015.08.018
[3] D. Zhou, T. Wu, K. Emmer, R. Kurupati, S. Tuyishime, Y. Liet al., Hexon-modified recombinant e1-deleted adenovirus vectors as dual specificity vaccine carriers for influenza virus, Molecular Therapy, vol. 21, no. 3, p. 696-706, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2012.248
[4] R. Kauffman and H. Ginsberg, Characterization of a temperature-sensitive, hexon transport mutant of type 5 adenovirus, Journal of Virology, vol. 19, no. 2, p. 643-658, 1976. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.19.2.643-658.1976
[5] R. Khare, V. Reddy, G. Nemerow, & M. Barry, Identification of adenovirus serotype 5 hexon regions that interact with scavenger receptors, Journal of Virology, vol. 86, no. 4, p. 2293-2301, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.05760-11
[6] K. Mukantayev, K. Tursunov, D. Kanayev, L. Tokhtarova, Y. Ramankulov, & K. Mukanov, Obtaining strain-producer of recombinant hexon of bovine adenovirus type 3, Eurasian Journal of Applied Biotechnology, no. 1, 2019. https://doi.org/10.11134/btp.1.2019.9
[7] X. Yuan, Y. Wang, W. Jin, B. Zhao, C. Chen, J. Yanget al., Structure-based high-throughput epitope analysis of hexon proteins in b and c species human adenoviruses (hadvs), Plos One, vol. 7, no. 3, p. e32938, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032938
[8] Y. Wang, Z. Zhang, L. Shang, H. Gao, X. Du, F. Liet al., Immunological study of reconstructed common ancestral sequence of adenovirus hexon protein, Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 12, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.717047
[9] L. Crawford-Miksza and D. Schnurr, Analysis of 15 adenovirus hexon proteins reveals the location and structure of seven hypervariable regions containing serotype-specific residues, Journal of Virology, vol. 70, no. 3, p. 1836-1844, 1996. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.70.3.1836-1844.1996
[10] H. Wodrich, T. Guan, G. Cingolani, D. Seggern, G. Nemerow, & L. Gerace, Switch from capsid protein import to adenovirus assembly by cleavage of nuclear transport signals, The Embo Journal, vol. 22, no. 23, p. 6245-6255, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg614