ELISA Kits for Epigenetics Research
Epigenetics research focuses on the regulation of gene activity and expression. It refers to heritable changes in gene expression that occur without alterations in the gene sequence. These changes are dynamic and reversible. Epigenetic research encompasses various molecular mechanisms, including DNA methylation, histone modification, chromatin remodeling, non-coding RNAs, and more. These molecular mechanisms can transmit genetic information within cells, activating or inhibiting gene expression, thereby influencing an organism's growth, development, health, and disease progression.
CUSABIO is dedicated to providing researchers with high-precision, high-sensitivity ready-to-use epigenetics ELISA kits that cater to a variety of sample types. These kits assist in the in-depth analysis of key regulatory mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone modifications, chromatin remodeling, and non-coding RNA, offering accurate and reliable data support for your scientific research. We aim to empower you to achieve breakthroughs in the field of epigenetics.
DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a chemical modification process where methyl groups are added to the genomic DNA molecules under the action of DNA methyltransferases, and it is the most important form of epigenetic modification. In eukaryotes, there are primarily two types of DNA methyltransferases, namely DNMT1 (DNA methyltransferase 1) and DNMT3a and DNMT3b. DNA methylation can affect chromatin structure, the accessibility of gene promoters, and the interaction between transcription factors and DNA. It plays a crucial role in biological processes such as cell differentiation, gene silencing, maintenance of genome stability, and responses to the environment.
Aberrant DNA methylation is closely associated with the development of cancer. On one hand, a decrease in the overall level of genome methylation can lead to the activation of proto-oncogenes, abnormal transposon expression, and genome instability, promoting tumorigenesis. On the other hand, abnormal high methylation in CpG islands (cytosine-phosphate-guanine) within gene promoter regions can result in gene silencing, leading to decreased expression of tumor suppressor genes and also contributing to the formation and progression of tumors. High methylation in certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer, can serve as a biomarker for early diagnosis.
Histone modification
DNA exists in the form of chromatin in the cell nucleus, and apart from DNA, chromatin also contains histones, non-histone proteins, and a small amount of RNA. Histones are the fundamental structural proteins of chromatin, found in the chromatin of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Histone modification refers to post-translational modifications of histones, such as methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and phosphorylation, which occur under the action of specific enzymes. These modifications are reversible covalent changes, and their occurrence, removal, and functional effects are mainly regulated by histone-modifying enzymes and corresponding cofactors, including three major categories: Writers, Erasers, and Readers.
Histone modifications not only regulate gene expression but also influence the development of various diseases, including some immune-related diseases and cancers. Lower levels of histone methylation or acetylation are associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer, lung cancer, and kidney cancer. Conversely, higher levels of specific histone modifications (such as H3K9ac) are correlated with lower survival rates in lung cancer [1].
Table 1. Main histone modifying enzymes of Writer and Eraser
| Modification type |
Writer |
Eraser |
| Methylate |
Histone lysine methyltransferases (HKMTs) and protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) |
lysine-specific demethylase 1 (KDM1/LSD1) and demethylase containing Jumonji C domain (JMJ) |
| Acetylization |
Histone acetyltransferase (HATs) |
Histone deacetylase (HDACs) |
| Phosphorylation |
Kinases |
Phosphatases |
Chromatin remodeling
Chromatin remodeling refers to the phenomenon where the packaging state of chromatin, the histones within nucleosomes, and the corresponding DNA molecules undergo a series of changes, resulting in alterations in the position and structure of chromatin. The mechanisms involved typically include histone modifications and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling refers to the use of ATP hydrolysis energy to move, loosen, evict, or rebuild nucleosomes, thereby regulating the packaging state of chromatin.
Chromatin remodeling can regulate gene transcription and is involved in normal cellular growth and development. However, abnormal chromatin remodeling can lead to the development of diseases such as cancer. For example, mutations in genes encoding chromatin remodeling complexes such as ARID1A, SMARCA4, SMARCB1, ACTL6A, CHRAC1, and RSF1 have been shown to be associated with various types of ovarian cancer [2].
Non-coding RNA
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) refers to RNA molecules that do not encode proteins. Functional non-coding RNAs mainly include miRNA, siRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA, among others.
1. MiRNA is a class of small ncRNAs, approximately 18 to 22 nucleotides in length, involved in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Their mechanism of action involves complementarity with mRNA, leading to mRNA silencing or degradation. Any changes in the structure and function of miRNA can potentially lead to the development of diseases, and some miRNAs that exhibit oncogenic functions are referred to as onco-miRs.
2. SiRNA, with a length of 20-25 nucleotides, exhibits strong specificity and can effectively inhibit the expression of target genes. It has a significant inhibitory effect on various cancers such as lung cancer and glioblastoma.
3. LncRNA is a class of ncRNAs with a length greater than 200 nucleotides, comprising 70%-98% of the total cellular RNA. They play roles in coordinating DNA methylation, chromatin structure remodeling, and histone chemical modifications, among others. The mechanism of action of lncRNAs still has many ambiguities, but research has found that some lncRNAs are highly sensitive in tumors, providing new insights into cancer treatment.
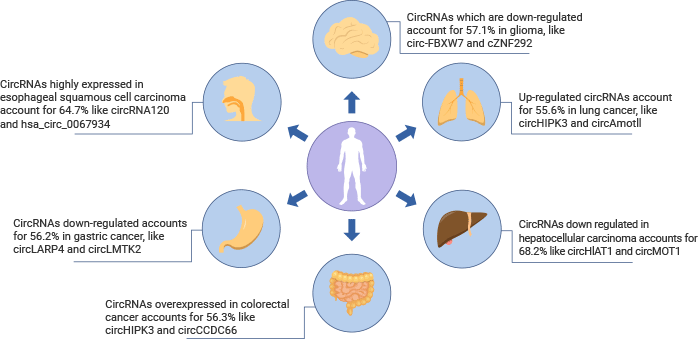
4. CircRNA is a type of circular RNA with a stable closed-loop structure. Due to its unique circular and stable structure, it not only plays important biological roles in the development processes of organisms, such as serving as miRNA sponges and functioning as endogenous RNAs, but also participates in the development of various diseases. CircRNA has become a new hotspot in the field of RNA research.
Fig 1. CircRNAs distribution in cancer [3]
The list of CUSABIO's epigenetics-related ELISA kits
| Code |
Product Name |
Sensitivity |
Target |
| CSB-EL002802HU |
Human Bromodomain-containing protein 4(BRD4) ELISA kit |
4.68 pg/mL |
BRD4 |
| CSB-EL004976HU |
Human Cytidine deaminase(CDA) ELISA kit |
3.9 pg/mL |
CDA |
| CSB-EL006590HU |
Human DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 protein(DDIT4) ELISA kit |
0.039 ng/mL |
DDIT4 |
| CSB-EL006710HU |
Human Protein DEK(DEK) ELISA kit |
5.86 pg/mL |
DEK |
| CSB-E09068h |
Human deoxyribonuclease Ⅰ,DNase-ⅠELISA Kit |
0.39 ng/mL |
DNASE1 |
| CSB-EL007049BO |
Bovine Deoxyribonuclease-1(DNASE1) ELISA kit |
3.1 pg/mL |
DNASE1 |
| CSB-EL007052HU |
Human Deoxyribonuclease gamma(DNASE1L3) ELISA kit |
5.86 pg/mL |
DNASE1L3 |
| CSB-EL007520HU |
Human Protein argonaute-2(EIF2C2) ELISA kit |
6.25 pg/mL |
EIF2C2 |
| CSB-EL007520MO |
Mouse Protein argonaute-2(EIF2C2) ELISA kit |
7.81 pg/mL |
EIF2C2 |
| CSB-EL007681HU |
Human Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3(ENPP3) ELISA kit |
0.039 ng/mL |
ENPP3 |
| CSB-EL009161HU |
Human Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD45 alpha(GADD45A) ELISA kit |
6.25 pg/mL |
GADD45A |
| CSB-E14145m |
Mouse growth arrest-specific gene-6(gas-6)ELISA Kit |
17.086 pg/mL |
GAS6 |
| CSB-EL010418HU |
Human Histone H3.1(HIST1H3A) ELISA kit |
5.8 pg/mL |
HIST1H3A |
| CSB-E08224r |
Rat High mobility group protein B1,HMGB-1 ELISA Kit |
|
HMGB1 |
| CSB-E13159h |
Human histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) ELISA kit |
1.56 μg/mL |
HRG |
| CSB-EL010736MO |
Mouse Histidine-rich glycoprotein(HRG) ELISA kit |
3.12 ng/mL |
HRG |
| CSB-EL011843MO |
Mouse Ubiquitin-like protein ISG15(ISG15) ELISA kit |
0.078 ng/mL |
ISG15 |
| CSB-E12075h |
Human ubiquitin-like modifier (ISG15) ELISA kit |
0.195 ng/mL |
ISG15 |
| CSB-EL011843BO |
Bovine Ubiquitin-like protein ISG15(ISG15) ELISA kit |
0.078 ng/mL |
ISG15 |
| CSB-EL012147HU |
Human Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1(KEAP1) ELISA kit |
6.25 pg/mL |
KEAP1 |
| CSB-EL012394HU |
Human Krueppel-like factor 4(KLF4) ELISA kit |
4.6 pg/mL |
KLF4 |
| CSB-E15769h |
Human melanoma-associated antigen 3 (MAGE-3) ELISA Kit |
0.156 ng/mL |
MAGEA3 |
| CSB-E09060h |
Human Metallothionein,MT ELISA Kit |
0.813 pg/mL |
MT |
| CSB-E09260h |
Human c-myc Oncogene product,c-myc ELISA Kit |
0.078 ng/mL |
MYC |
| CSB-EL015278HU |
Human N-myc proto-oncogene protein(MYCN) ELISA kit |
3.9 pg/mL |
MYCN |
| CSB-EL015319HU |
Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MYLIP(MYLIP) ELISA kit |
3.9 pg/mL |
MYLIP |
| CSB-EL015949HU |
Human Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1(NOTCH1) ELISA kit |
19.5 pg/mL |
NOTCH1 |
| CSB-EL017379MO |
Mouse Protein-arginine deiminase type-4(PADI4) ELISA kit |
1.17 pg/mL |
PADI4 |
| CSB-E16219h |
Human protein-arginine deiminase type-4(PADI4) ELISA kit |
0.039 ng/mL |
PADI4 |
| CSB-EL017722HU |
Human Protein disulfide-isomerase A4(PDIA4) ELISA kit |
5.8 pg/mL |
PDIA4 |
| CSB-E11308h |
Human protein(peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase)NIMA-interacting 1,PIN1 ELISA Kit |
0.39 pg/mL |
PIN1 |
| CSB-EQ027833HU |
Human RNA polymerase III (Pol III) antibody ELISA kit |
Request Information |
Pol III Ab |
| CSB-EL019571HU |
Human RE1-silencing transcription factor(REST) ELISA kit |
7.81 pg/mL |
REST |
| CSB-EL019798HU |
Human Ribonuclease 7(RNASE7) ELISA kit |
0.39 ng/mL |
RNASE7 |
| CSB-EL020818MO |
Mouse Secretoglobin family 3A member 1(SCGB3A1) ELISA kit |
15.6 pg/ml |
SCGB3A1 |
| CSB-EL020819MO |
Mouse Secretoglobin family 3A member 2(SCGB3A2) ELISA kit |
2.35 pg/mL |
SCGB3A2 |
| CSB-EL021142HU |
Human Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1(SFRS1) ELISA kit |
7.81 pg/mL |
SFRS1 |
| CSB-E16187m |
Mouse NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1(Sirt1)ELISA Kit |
0.039 ng/mL |
SIRT1 |
| CSB-E15058h |
Human NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1/SIR2L1) ELISA kit |
0.039 ng/mL |
SIRT1 |
| CSB-EL021339RA |
Rat NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1(SIRT1) ELISA kit |
8.5 pg/mL |
SIRT1 |
| CSB-E15058h-IS |
Human NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1/SIR2L1) ELISA kit |
0.156 ng/mL |
SIRT1 |
| CSB-E17018h |
Human NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-6 (SIRT6/SIR2L6) ELISA kit |
0.78 pg/mL |
SIRT6 |
| CSB-EL021860MO |
Mouse E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF1(SMURF1) ELISA kit |
7.8 pg/mL |
SMURF1 |
| CSB-E17858h |
Human thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) ELISA kit |
0.39 mU/mL |
TPMT |
| CSB-EL024502HU |
Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM63(TRIM63) ELISA kit |
3.1 pg/mL |
TRIM63 |
| CSB-E13238h |
Human Protein Gene Product 9.5 (PGP 9.5) ELISA Kit |
1.56 ng/mL |
UCHL1 |
| CSB-E11789h |
Human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase,WARS ELISA Kit |
0.078 ng/mL |
WARS |
| CSB-EL027165HU |
Human Zyxin(ZYX) ELISA kit |
5.8 pg/mL |
ZYX |
Research prospect of epigenetics
1. Early Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment: Epigenetics research helps us better understand the mechanisms of cancer development, which can aid in the development of more effective cancer treatments, including drug therapies targeting epigenetic modifications. Additionally, epigenetics can provide new biomarkers for the early diagnosis of cancer.
2. Precision Medicine: Epigenetics research provides additional tools and resources for precision medicine. By analyzing epigenetic markers in patients, doctors can gain a better understanding of disease risk, disease progression, and treatment responses, leading to more personalized treatment plans.
3. Environment and Health: Epigenetics also contributes to the study of how environmental factors impact health. Lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and dietary decisions can all regulate epigenetic modifications, influencing human health. This helps us better understand the interplay between environmental factors and genetics.
4. Brain Science: Epigenetics research is of significant importance in the field of neuroscience. It can help us better understand mechanisms related to neural development, learning and memory, and neurodegenerative diseases.
5. Aging and Longevity: Epigenetics research also touches on the mechanisms of human aging and longevity. Understanding the role of epigenetic modifications in the aging process can contribute to the search for methods to extend lifespan and improve elderly health.
In summary, the prospects for research in the field of epigenetics are very promising. It has the potential to make significant breakthroughs in areas such as medicine, life sciences, and environmental science, contributing to improved health, disease treatment, and scientific progress.
References:
[1] Fardi M, Solali S, Farshdousti Hagh M. Epigenetic mechanisms as a new approach in cancer treatment: An updated review[J]. Genes&Diseases, 2018, 5(4): 304-311.
[2] Ieva V, Rasa S, Rimantas J L, et al. The Emerging Role of Chromatin Remodeling Complexes in Ovarian Cancer[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(22).
[3] Cheng D, Wang J, Dong Z, et al. Cancer-related circular RNA: diverse biological functions[J]. Cancer Cell International, 2021, 21 (1): 11.