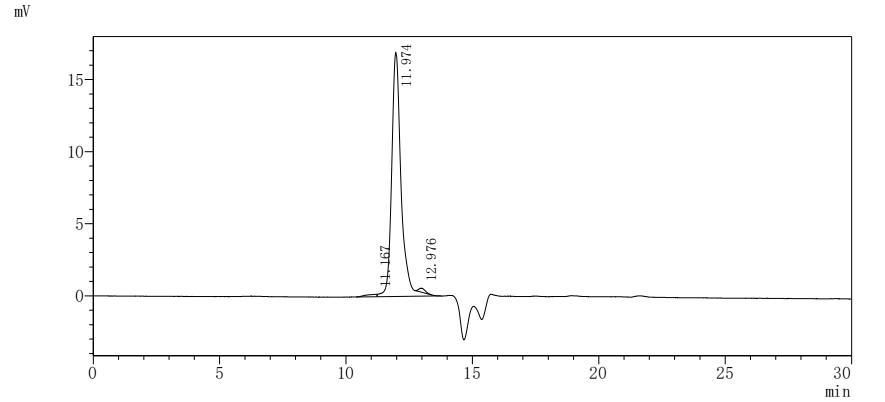
Recombinant Mouse Albumin (Alb) is produced in a yeast expression system, which appears to ensure consistent quality and reliability for research applications. The protein corresponds to the full-length mature sequence from amino acids 25 to 608, and includes an N-terminal 6xHis-tag for easy purification and detection. This product shows a purity level greater than 90%, as verified by SDS-PAGE, making it suitable for various experimental needs.
Albumin represents a crucial protein in the circulatory system. It's primarily responsible for maintaining osmotic pressure and transporting substances such as hormones, fatty acids, and drugs. In research contexts, albumin is widely studied for its role in metabolism, detoxification, and as a carrier protein. Its importance may extend to investigations into liver function and its involvement in various physiological pathways.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the recombinant Mouse Albumin is expressed in a Yeast expression system. Yeast systems are capable of producing properly folded eukaryotic proteins and can perform some post-translational modifications, though they may differ from mammalian systems in glycosylation patterns. The high purity (>90% by SDS-PAGE and >95% by SEC-HPLC) is noteworthy, as SEC-HPLC typically separates proteins based on size and shape, and a single peak suggests a homogeneous preparation, which often indicates proper folding. The protein contains the mature region (25-608aa) without the signal peptide. However, since activity is unverified, the protein cannot be guaranteed to be correctly folded or bioactive without functional validation. Mouse albumin's bioactivity includes binding capacity (e.g., fatty acids, drugs), which requires specific structural integrity.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Pull-Down Assays
The N-terminal 6xHis tag enables immobilization for pull-down assays, but this application is highly dependent on correct folding. If the albumin is properly folded, it could identify physiological binding partners (e.g., fatty acids, drugs, or other proteins). However, if misfolded, interactions may be non-physiological. The high purity reduces background, but folding should be validated (e.g., by ligand binding assays) before interpreting interaction data.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is well-supported. The recombinant albumin can serve as an effective immunogen for antibody generation, as antibodies often recognize linear epitopes that are less dependent on native folding. The high purity and mature protein sequence are suitable for immunization. However, if the protein is misfolded, antibodies may not recognize conformational epitopes of native mouse albumin in serum. Validation against native mouse serum albumin is recommended. The yeast expression system avoids mammalian-specific modifications, which could be an advantage for reducing cross-reactivity.
3. Comparative Protein Biochemistry and Species-Specific Studies
This application is appropriate and lower risk. Techniques like circular dichroism or dynamic light scattering can assess folding and stability without requiring functional activity. The defined mature region (25-608aa) allows for standardized comparisons with human or other albumins. The high purity by SEC-HPLC suggests a monodisperse solution, supporting reliable biophysical comparisons. This application can proceed even without activity validation, as it focuses on inherent protein properties.
4. Protein Purification Method Development
This application is valid. The His-tagged albumin can be used as a model protein for developing purification protocols, especially for albumin-like proteins. The high purity provides a benchmark for method optimization. The yeast expression background is relevant for developing methods to separate albumin from eukaryotic contaminants. This application is not dependent on bioactivity and can be pursued without folding validation.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Given the high purity and indication of monodispersity from SEC-HPLC, this recombinant mouse albumin is likely correctly folded, but functional validation is still recommended before relying on it for bioactivity-dependent applications. Prioritize its use in antibody development, comparative biochemistry, and purification method development, as these are lower risk. For protein-protein interaction studies, first confirm folding through ligand binding assays (e.g., with fatty acids or dyes like bromocresol green). If resources allow, test binding activity to validate bioactivity. The yeast-produced albumin may have glycosylation differences from native mouse albumin, so for critical comparative studies, confirm key properties against mammalian-derived albumin.