Th2 Cytokines
As mentioned on the article "T cell cytokine", Th2 cell is a subtype of CD4+ helper cells. Th2 helper cells are mainly immune responses against extracellular multicellular parasites. They are mainly induced by IL-4. The main cytokines for their execution are IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. The most important executive cells are mast cells and basophil. In addition, there are B cells that produce IgE and CD4+ T cells that secrete IL-4/IL-5. The main transcription factor is STAT6 and GATA3 and so on. IL-5 secreted by CD4+ T cells activates eosinophils, enabling them to attack extracellular parasites. In addition, IL-4 & IgE activates mast cells and releases histamine (serotonin), etc., causing tracheal contraction and diarrhea And intestinal peristalsis to expel parasites.
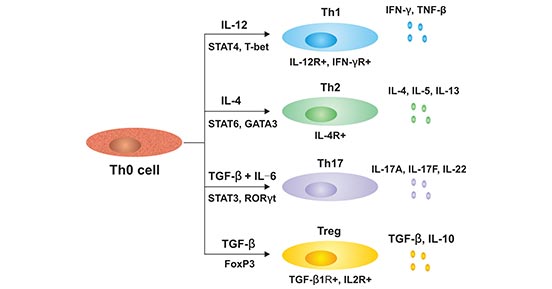
Figure 1. The subtyes of cells differentiated by Th0 cells.
In this article, we focus on the cytokines of Th2 cell differentiation and the cytokines secreted by Th2 cells.
The cytokines of Th2 Differentiation
As mentioned on the article entitled “Th1 cytokines”, Th2 cells are differentiated from Th0 cells. The differentiation direction of Th0 cells depends on the nature of the antigen and the hormones and cytokines in the local environment. For example, viral and intracellular parasite infections mainly induce differentiation into Th1 cells, while allergens (inducing allergic antigens) and parasite infections mainly induce differentiation into Th2 cells. The type of cytokines and the balance between cytokines also have an important regulatory effect on Th0 cells. IL-12 produced by macrophages in the innate immune response is an important cytokine that promotes differentiation into Th1 cells. IFN-γ secreted by natural killer cells (NK cells) not only promotes the secretion of IL-12 by macrophages, but also suppresses The proliferation of Th2 cells eventually leads to differentiation towards Th1 cells.
Th2 cell differentiation depends on IL-4, which is required for Th2 priming and maturation. It is also an autocrine of Th2 cells during their maturation, that is, IL-4 can be produced by Th2 cells itself. Morover, high concentration of IL-4 can block the generation of Th1 cells from naïve T cells. Besides IL-4, there are several cytokines in Th2 cell differentiation, including IL-2, IL-6, IL-27, IL17E, IL31 and IL33.
IL-2 is primarily expressed by activated T cells and mediates their proliferation and clonal expansion. IL-6 is released by APCs. It is a key factor that initiates maturation of Th2 cells from TH0 in conjunction with IL-4, and high concentration of IL-6 can block the generation of Th1 cells in a similar fashion to IL-4. IL-27 is produced by activated monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It synergizes with IL-12 to cause the production of IFNγ by naive Th cells and increases proliferation of cells without affecting memory T-cells. IL17E induces cytokine expression and helps maintain Th2 function. it plays a critical role in the formation of Th2 memory. IL31 is mainly produced by activated CD4+ cells and associated with enhanced IL-4 and IL-13 expression by Th2. IL33 is necessary for Th2 cytokine production.
The Cytokines Secreted by Th2 Cells
As mentioned earlier, Th2 cells mainly secrete IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. IL-4 secreted by Th2 cell can Inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of Th1 cells and stimulate B cell proliferation and maturation into plasma cells. Moreover, it also regulates the class switching of antibodies and increases IgE production. IL-5 produced by Th2 cell mainly attracts and activates eosinophils, and IL-3 assists in the recruitment and maintenance of basophils into lymphoid tissues in response to infection.
Actually, except for IL-4, IL-5 & IL-13, Th2 cells also are the source for IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17E and IL-31. IL-6 secreted by Th2 cells play a critical role in B cell maturation into IgG secreting cells. IL-10 can inhibit secretion of various cytokines by Th1 cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. IL-13 can stimulate B-cell production of IgE. It not only attracts basophils and mediates the release of granules, but also can trigger mast cells to release granules. IL-17E can co-mediate production IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13.
IL-31 secreted by Th2 cells can implicate in inflammatory responses in the skin, and recruit PMNs, monocytes, and T cells to the sites of infection.


