World Diabetes Day:
Diabetes across life stages
World Diabetes Day (WDD) is observed annually on November 14th, initiated in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO) to raise public awareness about diabetes. This day also commemorates the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting, one of the discoverers of insulin.
The theme for World Diabetes Day in 2025 is "Diabetes across life stages", recognizes that every person living with diabetes should have access to integrated care, supportive environments and policies that promote health, dignity and self-management.
1. What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar, resulting from absolute or relative insulin deficiency and impaired insulin utilization. It can be categorized into four types:
1.1 Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM)
T1DM is a chronic metabolic endocrine disorder where the pancreas' beta cells are destroyed, leading to an absolute lack of insulin. This destruction is typically mediated by the immune system, which mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells. Consequently, patients are unable to produce sufficient insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels. (click "Autoimmune Disease Series: Type 1 Diabetes" for more information)
1.2 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)
T2DM is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% to 95% of all diabetes cases. Unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes is primarily the result of decreased insulin sensitivity (insulin resistance) and a gradual decline in insulin secretion from beta cells. Possible contributing factors include genetics, lifestyle, age, and ethnic or racial background.
1.3 Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
GDM refers to the abnormal glucose tolerance first discovered or diagnosed during pregnancy. It typically occurs at any stage of pregnancy but is most often identified in the second or third trimester. The main mechanism of GDM is insulin resistance, which may be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, obesity, poor dietary habits, and lifestyle. Additionally, pregnancy itself increases insulin demand, potentially leading to poor blood glucose control. Women with a history of GDM are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes postpartum.
1.4 Other Specific Types of Diabetes
These are all forms of diabetes caused by factors other than type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes. Classified by etiology, other specific types can be divided into several subcategories, including monogenic defects in beta cell function, pancreatogenic diabetes, drug- or chemical-induced diabetes, endocrine diseases, monogenic defects in insulin action, genetic syndromes associated with diabetes, infections, and rare forms of immune-mediated diabetes. Among these, monogenic defects in beta cell function and pancreatogenic diabetes are relatively common subcategories.
2. The latest research advancements in diabetes
Currently, scientists have made a series of significant progress in diabetes research, encompassing everything from blood sugar control medications and insulin therapies to innovative diabetes management devices, as well as potential therapies like immunotherapy and beta cell regeneration. Here are some of the latest research developments:
2.1 Pharmacological Advances
SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, among other novel hypoglycemic drugs, have been proven to effectively lower blood glucose and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The American Diabetes Association (ADA) emphasized the importance of these drugs in its 2024 clinical practice standards [1]. For instance, new drugs like empagliflozin have shown excellent performance in improving blood glucose control in adults with T2DM and have demonstrated potential applications in obesity, cardiovascular risk-related diseases, and diabetic nephropathy.
Additionally, researchers are developing more effective insulin formulations, such as long-acting and rapid-acting insulins, to better mimic the natural secretion pattern of insulin and help patients control blood glucose levels more effectively.
2.2 Disease Classification and Personalized Treatment
Researchers have identified different subtypes of type 2 diabetes, including Severe Insulin Deficiency Diabetes (SIDD), Severe Insulin Resistance Diabetes (SIRD), Mild Obesity-Related Diabetes (MOD), and Mild Age-Related Diabetes (MARD). The identification of these subtypes provides a scientific basis for personalized treatment strategies [2].
2.3 Early Diagnosis and Screening
Early diagnosis and screening of islet autoantibodies are crucial directions in the early diagnosis research of type 1 diabetes, aiding in earlier diagnosis and intervention [3]. The application of continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGM) and automated insulin delivery systems is transforming the management of type 1 diabetes, enhancing patients' self-management abilities and treatment adherence [4]. New devices such as continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and smart insulin pumps can monitor blood glucose levels in real-time and automatically adjust insulin delivery, providing patients with more convenient and efficient management tools.
2.4 Other Research Progress
Recent studies show that non-endocrine tissues can be reprogrammed to respond to blood glucose changes without the use of insulin, offering new possibilities for diabetes treatment. Advances in genomics have deepened our understanding of beta cell function, aiding in the identification of diabetes susceptibility genes and propelling the development of personalized medicine. Analyzing an individual's lipid profile can assess their risk of diabetes and inform the development of corresponding prevention and treatment strategies.
Read more:
Diabetes: What You Need to Know Before Starting Research?
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
3. Diabetes Research Related Products from CUSABIO
To aid in your research of diabetes-related biomarkers and signaling pathways, to comprehend the pathogenesis of diabetes, assess the progression of the disease, and develop novel therapeutic approaches, CUSABIO has meticulously assembled a suite of commonly utilized proteins, antibodies, and ELISA kits in diabetes research. The targets encompass, but are not limited to, insulin (INS) and its receptor (INSR), islet beta cell markers such as GLUT2 and PDX1, inflammatory markers including TNF-α, IL-6, and CRP, oxidative stress markers like 8-OHdG and MDA, and molecules associated with the insulin signaling pathway such as IRS1/2.
● Hot Targets in Diabetes Research
● CUSABIO Recombinant Proteins for Diabetes Research
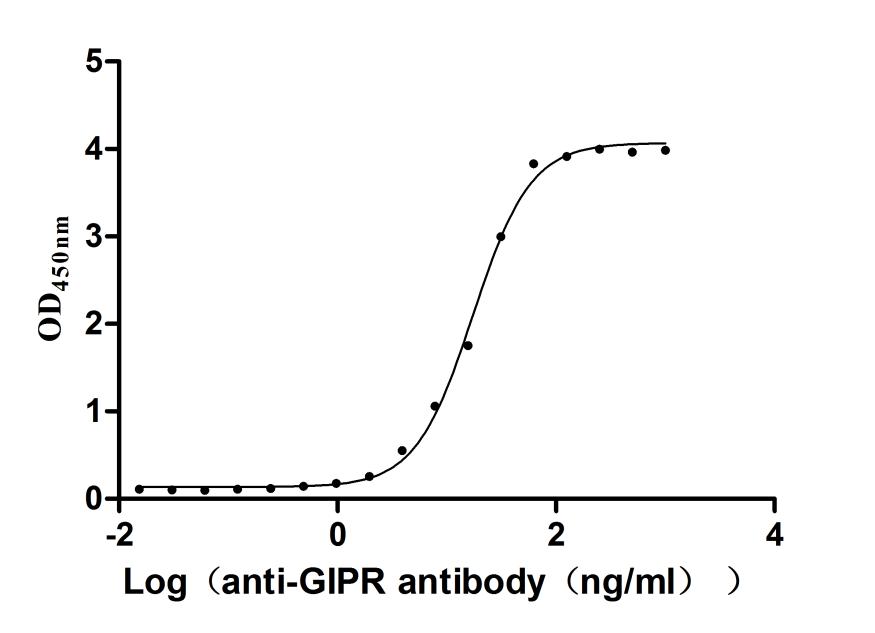
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human GIPR at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-GIPR recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009438MA1HU),the EC50 16.18-18.70 ng/mL.
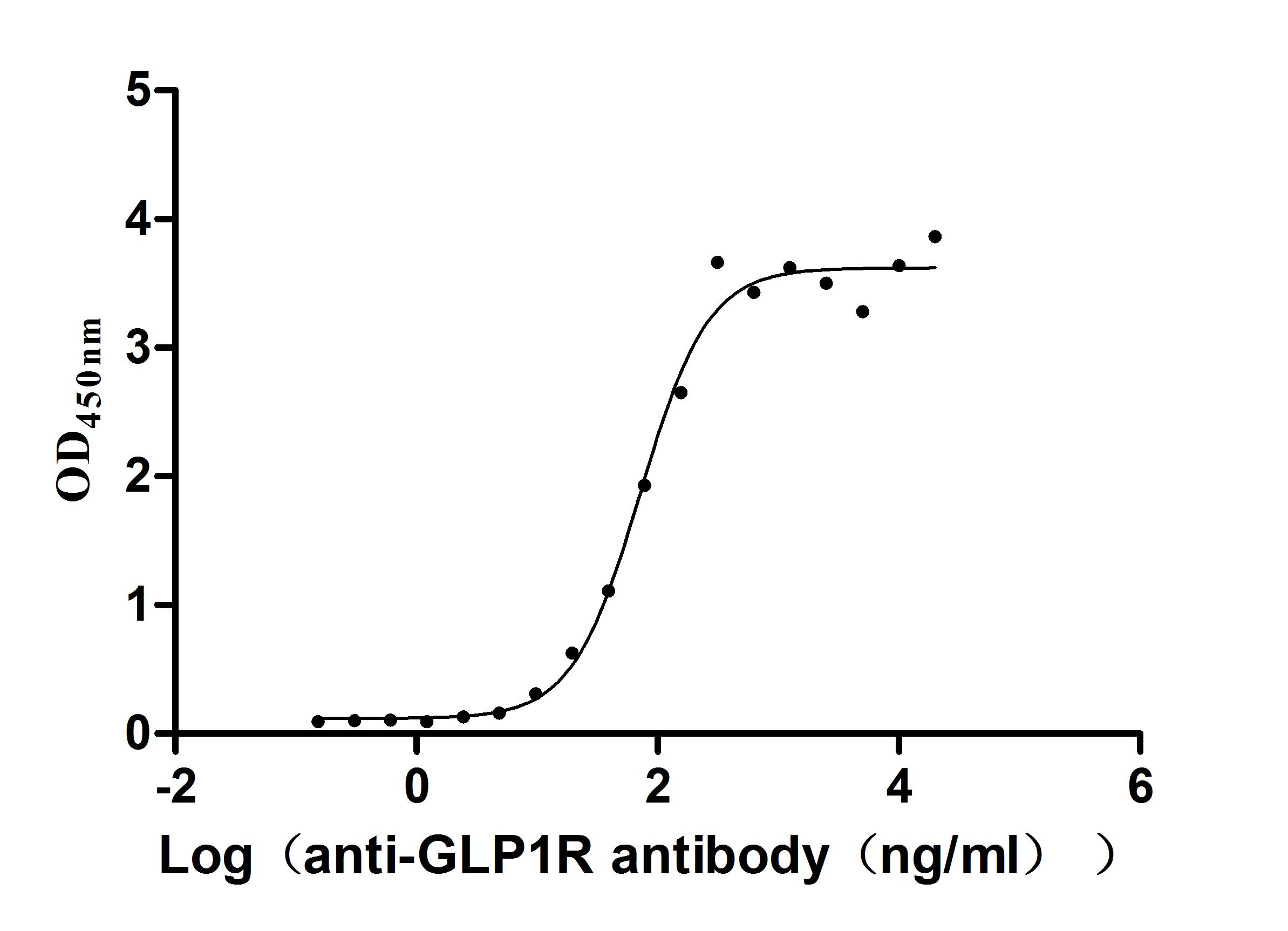
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human GLP1R at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-GLP1R recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009514MA1HU), the EC50 is 54.54-94.23 ng/mL.
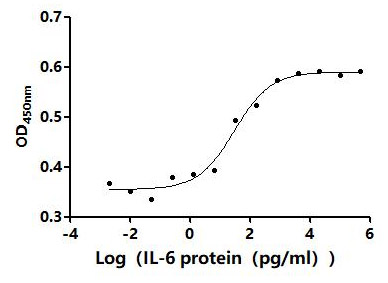
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human IL6 at 2μg/mL can bind Anti-IL6 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA011664MA1HU),the EC50 is 35.80-41.82 ng/mL.
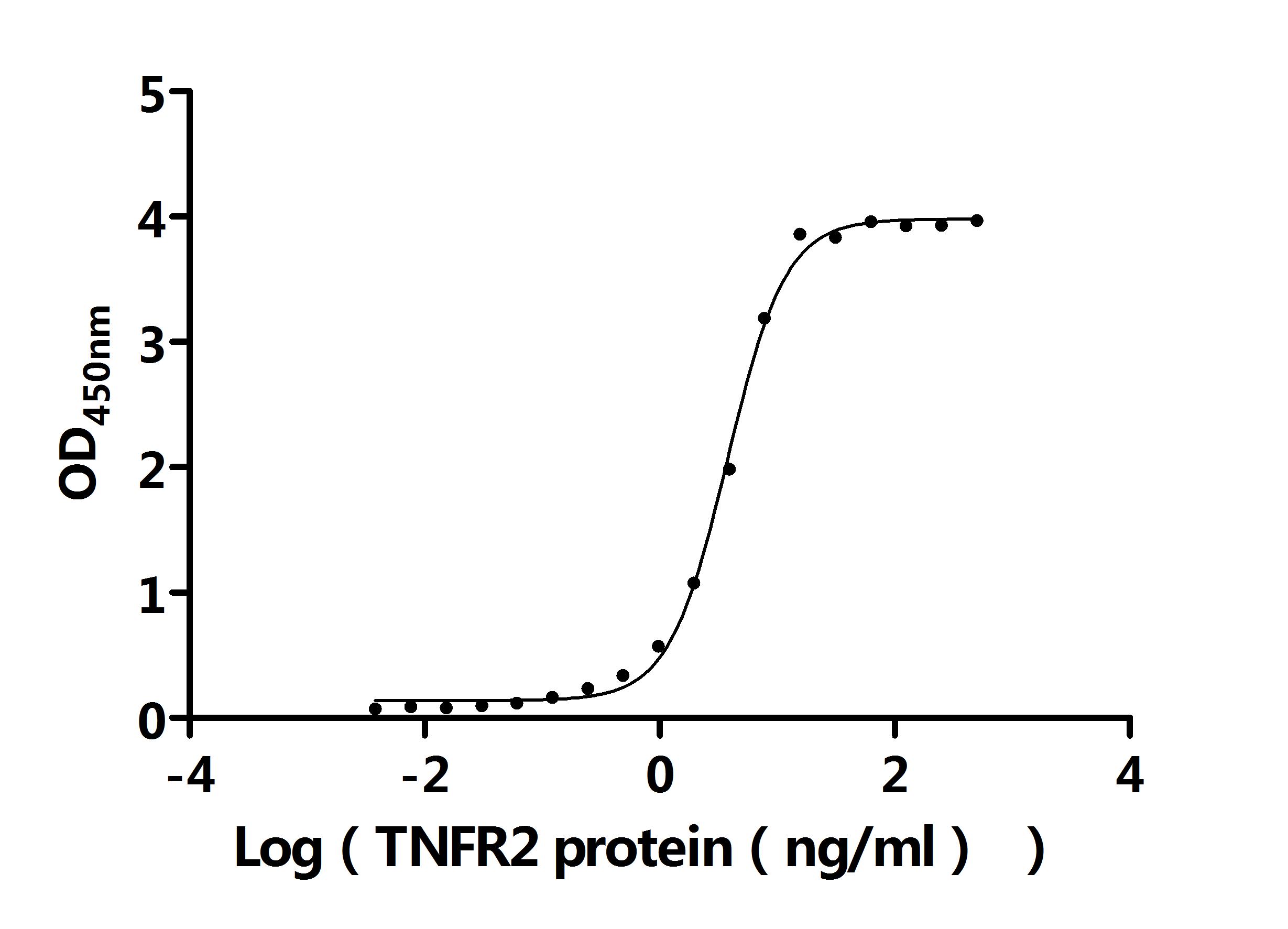
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human TNF at 5 μg/ml can bind Human TNFR2 protein (CSB-MP023978HU2). The EC50 is 3.470-4.107 ng/mL.
| Target |
Product Name |
Source |
Tag Info |
Product Code |
| ADIPOQ |
Recombinant Bovine Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged |
CSB-EP661101BO |
| Adipoq |
Recombinant Mouse Adiponectin (Adipoq) |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-EP723362MO |
| Adipoq |
Recombinant Mouse Adiponectin (Adipoq), partial |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-RP079474m |
| ADIPOQ |
Recombinant Bovine Adiponectin (ADIPOQ) |
Yeast |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-YP661101BO |
| ADIPOQ |
Recombinant Horse Adiponectin D (ADIPOQ), partial |
E.coli |
Tag-Free |
CSB-EP4093HO |
| AKT1 |
Recombinant Human RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) |
E.coli |
N-terminal GST-tagged |
CSB-EP001553HU |
| Akt1 |
Recombinant Rat RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (Akt1) |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-EP001553RA |
| Alb |
Recombinant Mouse Serum albumin (Alb) |
Baculovirus |
C-terminal 9xHis-tagged |
CSB-BP001561MO |
| ALB |
Recombinant Dog Serum albumin (ALB) |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-EP001561DO |
| ALB |
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis albumin (ALB) |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged |
CSB-EP001561MOV |
| ALB |
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis albumin (ALB) |
Mammalian cell |
N-terminal 6xHis-Myc-tagged |
CSB-MP001561MOV |
| ALB |
Recombinant Dog Serum albumin (ALB) |
Yeast |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-YP001561DO |
| Alb |
Recombinant Mouse Albumin (Alb) |
Yeast |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-YP001561MO |
| ALB |
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis albumin (ALB) |
Yeast |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-YP001561MOV |
| ALB |
Recombinant Bovine Serum albumin (ALB) |
Yeast |
C-terminal 6xHis-Myc-tagged |
CSB-YP001561BO |
| ALB |
Recombinant Bos taurus Albumin (ALB) |
Baculovirus |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-BP001561BO |
| Alb |
Recombinant Rat Serum albumin (Alb), Biotinylated |
E.coli |
N-terminal MBP-tagged and C-terminal 6xHis-Avi-tagged |
CSB-EP001561RA-B |
| ALB |
Recombinant Chicken Serum albumin (ALB), partial |
Yeast |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-YP001561CH |
| ALB |
Recombinant Chicken Albumin (ALB), partial |
E.coli |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
CSB-EP001561CH |
| Alb |
Recombinant Rat Serum albumin (Alb) |
E.coli |
N-terminal 6xHis-tagged and C-terminal Avi-tagged |
CSB-EP001561RA |
● CUSABIO Antibodies for Diabetes Research
Tested Applications:
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP
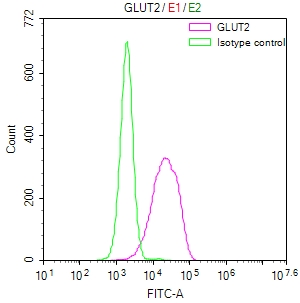
Tested Applications:
ELISA, IHC, IF, FC
Tested Applications:
ELISA, IHC
Tested Applications:
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
- Recombinant Antibody
| Target |
Product Name |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
Code |
| AKT1 |
Phospho-AKT1 (T450) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-RA001553A450phHU |
| AKT1 |
Phospho-AKT1 (Ser473) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP |
CSB-RA001553A473phHU |
| AKT1 |
AKT1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
CSB-RA917625A0HU |
| ALB |
ALB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, FC |
CSB-RA264109A0HU |
| CRP |
CRP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA988767A0HU |
| DPP4 |
DPP4 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA927191A0HU |
| GCG |
GCG Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-RA009315A0HU |
| Gipr |
Gipr Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Mouse, Rat |
ELISA |
CSB-RA009438MA1MO |
| GIPR |
GIPR Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-RA009438MA2HU |
| GIPR |
GIPR Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human, Macaca fascicularis |
ELISA |
CSB-RA009438MA1HU |
| GLP1R |
GLP1R Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-RA009514MA1HU |
| IL6 |
IL6 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-RA011664MA1HU |
| INS |
INS Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA584163A0HU |
| INSR |
INSR Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IF |
CSB-RA155156A0HU |
| SLC2A2 |
SLC2A2 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC, IF, FC |
CSB-RA438622A0HU |
- Monoclonal Antibody
| Target |
Product Name |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
Code |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-MA079461A0m |
| AKT1 |
AKT1 Monoclonal Antibody |
Human,Mouse,Pig,Rat |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-MA011037 |
| ALB |
ALB Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-MA076752 |
| CRP |
CRP Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-MA027411E0m |
| GCG |
GCG Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-MA935920 |
| IL1B |
IL1B Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-MA065741A0m |
| IL1B |
IL1B Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, ICC |
CSB-MA010884 |
| IL6 |
IL6 Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-MA067571A0m |
| PPARG |
PPARG Monoclonal Antibody |
Human,Dog,Pig,Rat,Mouse |
ELISA, WB, ICC |
CSB-MA930213 |
| TNF |
TNF Monoclonal Antibody |
Bovine |
ELISA |
CSB-MA084771A0m |
| TNF |
TNF Monoclonal Antibody |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-MA080271 |
| TNF |
TNF Monoclonal Antibody |
Human,Mouse,Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-MA080272 |
- Polyclonal Antibody
| Target |
Product Name |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
Code |
| Adipoq |
Adipoq Antibody |
Mouse |
ELISA |
CSB-PA07946A0Rb |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-PA07956A0Rb |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-PA07957A0Rb |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-PA618019YA01HU |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Bovine |
ELISA |
CSB-PA661101LA01BO |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Bovine |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA661101YA01BO |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA000014 |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA000806 |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-PA293186 |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA149289 |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA938581 |
| ADIPOQ |
ADIPOQ Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA828343 |
| AKT1 |
AKT1 Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP |
CSB-PA15905A0Rb |
| AKT1 |
AKT1 Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
CSB-PA000852 |
| AKT1 |
Phospho-AKT1 (S124) Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-PA008118 |
| AKT1 |
Phospho-AKT1 (T72) Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-PA008120 |
| AKT1 |
AKT1 Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-PA008122 |
| AKT1 |
AKT1 Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
WB |
CSB-PA080256 |
| AKT1 |
Phospho-AKT1 (S129) Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA000645 |
| AKT1 |
Phospho-AKT1 (T308) Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB |
CSB-PA000657 |
● CUSABIO ELISA Kits for Diabetes Research
| Target |
Product Name |
Sample Types |
Detection Range |
Code |
| ADIPOQ |
Bovine adiponectin,ADP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
3.125 μg/mL-50 μg/mL |
CSB-E14054B |
| ADIPOQ |
Sheep adiponectin (ADIPOQ)ELISA kit |
serum, plasma |
6.25 ng/mL-100 ng/mL |
CSB-EL001366SH |
| ADIPOQ |
Hamster adiponectin, C1Q and collagen domain containing (ADIPOQ)ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.469 ng/mL-30 ng/mL |
CSB-EL001366HA |
| AKT1 |
Human RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase(AKT1) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, cell lysates |
0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL |
CSB-EL001553HU |
| ALB |
Mouse Albumin (Alb)ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.781 μg/mL-200 μg/mL |
CSB-E13878m |
| ALB |
Pig Albumin (Alb) ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, urine |
0.03 μg/mL-7000 μg/mL |
CSB-E16207p |
| ALB |
Goat Albumin (Alb)ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.17 μg/mL-350 μg/mL |
CSB-E15758G |
| ALB |
Dog Albumin(Alb) ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.273 μg/mL-35 μg/mL |
CSB-E15757c |
| ALB |
Sheep Albumin (Alb)ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates,Urine, Tissue Homogenates |
350 μg/mL-21.88 μg/mL |
CSB-E15839Sh |
| ALB |
Bovine Albumin(Alb) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.313 μg/mL-80 μg/mL |
CSB-E08664b |
| ALB |
Horse Albumin(Alb) ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma |
1.25 μg/mL-80 μg/mL |
CSB-E16205Hs |
| ALB |
Guinea Pig Albumin(Alb) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.156 μg/mL-10 μg/mL |
CSB-E15765Gp |
| ALB |
Rabbit Albumin(Alb) ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, urine |
0.273 μg/mL-70 μg/mL |
CSB-E16204Rb |
| CRP |
Rat C-Reactive Protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates, cell lysates |
31.25 ng/mL-2000 ng/mL |
CSB-E07922r |
| CRP |
Mouse C-Reactive Protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates |
15.6 ng/mL-1000 ng/mL |
CSB-E07923m |
| CRP |
Rabbit C-Reactive Protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma |
7.8 pg/mL-2000 pg/mL |
CSB-E06847Rb |
| CRP |
Pig C-reactive protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.625 ng/mL-40 ng/mL |
CSB-E08163p |
| CRP |
Canine C-Reactive Protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates |
0.312 μg/mL-20 μg/mL |
CSB-E14262c |
| CRP |
Mouse C-Reactive Protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
5 ng/mL-4000 ng/mL |
CSB-E07923m(1) |
| CRP |
Bovine C-reactive protein,CRP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma |
1.25 ng/mL-80 ng/mL |
CSB-E08577b |
Reference:
[1] Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care, 2024.
[2] Translating Subphenotypes of Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes from Cohort Studies to Electronic Health Records in the United States. medRxiv, 2024.
[3] Islet Autoantibody Levels Differentiate Progression Trajectories in Individuals With Presymptomatic Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes, 2022.
[4] Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control. Diabetes Metab J, 2023.