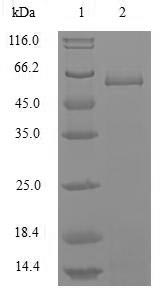
Intact influenza B virus nucleoprotein (NP) cDNA (1-560aa) with an N-terminal 10xHis-tag was expressed in the Baculovirus cells. The forming protein is the recombinant full-length influenza B virus NP protein. The purity of this protein is greater than 85% determined by SDS-PAGE. Under reducing conditions, the gel showed a molecular weight band of about 65 kDa. In-stock influenza B virus NP proteins are offered now. In addition to producing specific antibodies, this recombinant influenza B virus NP protein may be used in the studies of microbiology.
Nucleoprotein (NP) is the predominant component of the influenza virus ribonucleoprotein. It is highly conserved among each type of influenza viruses. Alice Labaronne etc. demonstrated that the NP of influenza B virus has a long N-terminal tail of 70 residues with intrinsic flexibility. This tail contains the Nuclear Location Signal (NLS). And NP is imported into the nucleus by the importin-α/β pathway via direct interaction with importin-α isoforms. In addition, NP is the potential target for a universal influenza vaccine.