International Rare Disease Day
Not-So-Rare Rare Diseases
February 29th, 2008, marked the first International Rare Disease Day, initiated and organized by the European Organization for Rare Diseases (EURORDIS). This day, occurring once every four years, symbolizes the rarity of these conditions.
Globally, approximately 7,000 types of rare diseases have been identified, with about 250 new ones added each year. The total number of patients worldwide exceeds 300 million. In China, the patient population is also significant, with around 20 million individuals affected and over 200,000 new cases reported annually. Despite being defined as having a low incidence rate, rare diseases are not uncommon due to its large population and deserve increased public attention.
1. What are Rare Diseases?
Rare diseases, also known as "orphan diseases," are characterized by their extremely low incidence rates. However, the specific criteria for defining rare diseases vary across different countries and regions. In the United States, a rare disease is one that affects fewer than 200,000 people or has an incidence rate lower than 1 in 1,500. The European Union defines it as a disease with an incidence rate not exceeding 5 in 10,000. In Japan, diseases with fewer than 50,000 patients or an incidence rate lower than 1 in 2,500 are considered rare. In China, there is currently no unified official definition, but the World Health Organization (WHO) standard is generally followed, which classifies diseases with a prevalence of 0.65‰ to 1‰ of the total population as rare diseases.
2. Causes of Rare Diseases
The causes of rare diseases can be mainly attributed to genetic and environmental factors. About 80% of rare diseases are caused by genetic factors, which are passed on through autosomal dominant, recessive, or X-linked inheritance patterns and are primarily caused by gene mutations involving single or multiple genes. Environmental factors, such as exposure to chemicals, radiation, and viral infections, can also induce gene mutations leading to rare diseases. Additionally, the lifestyle, diet, and exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy can increase the risk of the fetus developing a rare disease.
3. Characteristics of Rare Diseases
Rare diseases are characterized by low incidence rates, severe conditions, diagnostic difficulties, and limited treatment options. Due to their rarity, clinical doctors often have limited knowledge about these diseases. Most rare diseases manifest in childhood and progress over time, causing significant damage to patients' physical functions and even posing life-threatening risks. The complex nature of rare diseases makes the diagnostic process lengthy and challenging, often requiring patients to visit multiple hospitals to confirm their condition, which can delay treatment opportunities. Currently, effective treatment methods for rare diseases are relatively limited, leaving many patients without available medications, and some treatment drugs are prohibitively expensive, placing a heavy financial burden on patients' families.
4. Classification of Rare Diseases
4.1 Classification by Organ System
- Nervous System Rare Diseases: Huntington's disease, spinal muscular atrophy, hereditary spastic paraplegia, tuberous sclerosis, neurofibromatosis, etc.
- Blood System Rare Diseases: Thalassemia, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, Gaucher's disease, hereditary spherocytosis, Glanzmann's thrombasthenia, etc.
- Endocrine System Rare Diseases: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, congenital hypothyroidism, idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, Type 1 diabetes, etc.
- Immune System Rare Diseases: Primary immunodeficiency diseases, severe combined immunodeficiency, autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, autoimmune inflammatory diseases, common variable immunodeficiency,
etc.
4.2 Classification by Inheritance Pattern
- Autosomal Dominant Rare Diseases: Marfan syndrome, neurofibromatosis, familial hypercholesterolemia, polycystic kidney disease, osteogenesis imperfecta, etc.
- Autosomal Recessive Rare Diseases: Cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria, fragile X syndrome, muscular dystrophy, Tay-Sachs disease, etc.
- X-linked Rare Diseases: Hemophilia A, red-green color blindness, fragile X syndrome, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, etc.
4.3 Classification by Pathogenesis
- Monogenic Rare Diseases: Sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, Marfan syndrome, etc.
- Polygenic Rare Diseases: Congenital heart disease, polycystic kidney disease, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, etc.
- Chromosomal Abnormality Rare Diseases: Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, 5p deletion syndrome, etc.
5. Progress in Rare Disease Drug Research and Development
In recent years, with the deepening of research on rare diseases and continuous technological advancements, significant progress has been made in the development of rare disease drugs. An increasing number of new drugs have entered clinical trial phases, and some have been successfully approved for marketing, bringing hope to patients with rare diseases. Here are some rare disease drug targets and related research progress:
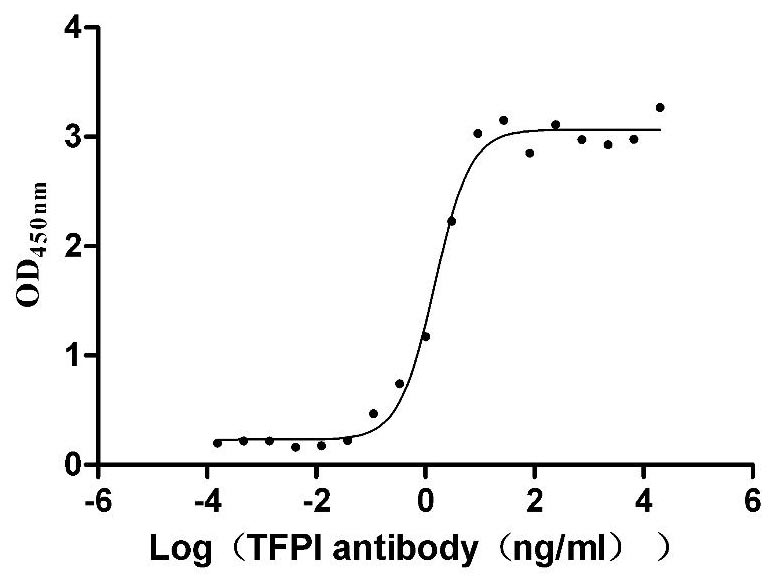
- TFPI: Pfizer's innovative drug HYMPAVZI™ has been approved by the FDA for routine treatment of hemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency) or hemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency) in patients aged 12 and above without factor inhibitors, to reduce bleeding episodes. HYMPAVZI is the first and only approved antithrombin pathway inhibitor for the treatment of hemophilia A and B in the United States and is also the first hemophilia innovative therapy administered via a prefilled autoinjector in the country.
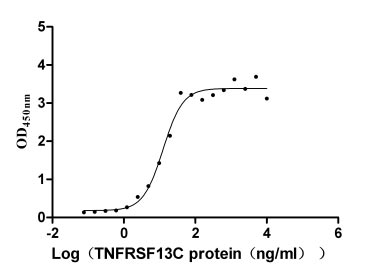
- TNFRSF13C: This target is related to multiple autoimmune diseases and lymphatic system diseases. Currently, drug research and development targeting this receptor are mostly in the preclinical research stage, mainly focusing on regulating the activity of the receptor to control the activation and differentiation of B cells, thereby improving disease symptoms. The diseases under investigation include warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia, systemic sclerosis, primary Sjögren's syndrome, and marginal zone B-cell lymphoma.
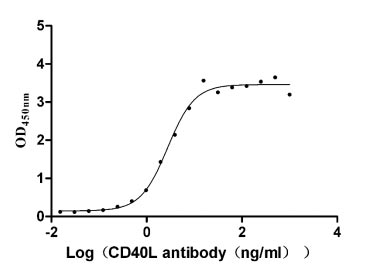
- CD40LG: CD40LG plays a key role in some rare immune deficiency diseases and autoimmune diseases. Currently, some monoclonal antibody drugs targeting CD40LG are in the early stages of clinical trials, aiming to block the binding of CD40LG and CD40, regulate the function of immune cells, and restore normal immune balance.
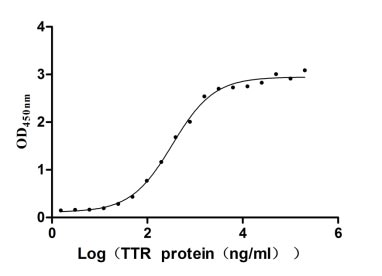
- TTR: In the rare disease of transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR), TTR is a key target. Several drugs have been approved for marketing, such as Pfizer's tafamidis, which stabilizes the structure of TTR, prevents its misfolding and aggregation, and thus delays disease progression. Additionally, some drugs under investigation, such as ASO and siRNA drugs, aim to reduce TTR expression at the genetic level, providing more treatment options for ATTR patients.
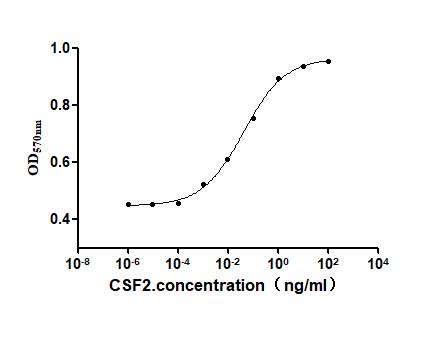
- CSF2: CSF2 plays an important role in regulating the proliferation, differentiation, and function of immune cells. Drug research and development targeting the CSF2 receptor mainly focuses on some rare immune deficiency diseases and autoimmune diseases. Currently, some small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies are in the preclinical research or early clinical trial stages, inhibiting the signal transduction of CSF2 to regulate the activity of immune cells and improve disease symptoms.
- MAPT: In some neurodegenerative rare diseases, such as frontotemporal dementia, the abnormal aggregation of MAPT protein is an important pathological feature. Currently, drug research and development targeting the MAPT receptor mainly focuses on inhibiting the aggregation of tau protein, promoting its degradation, and regulating its phosphorylation levels. Some small molecule compounds and antibody drugs are in the preclinical research and early clinical trial stages.
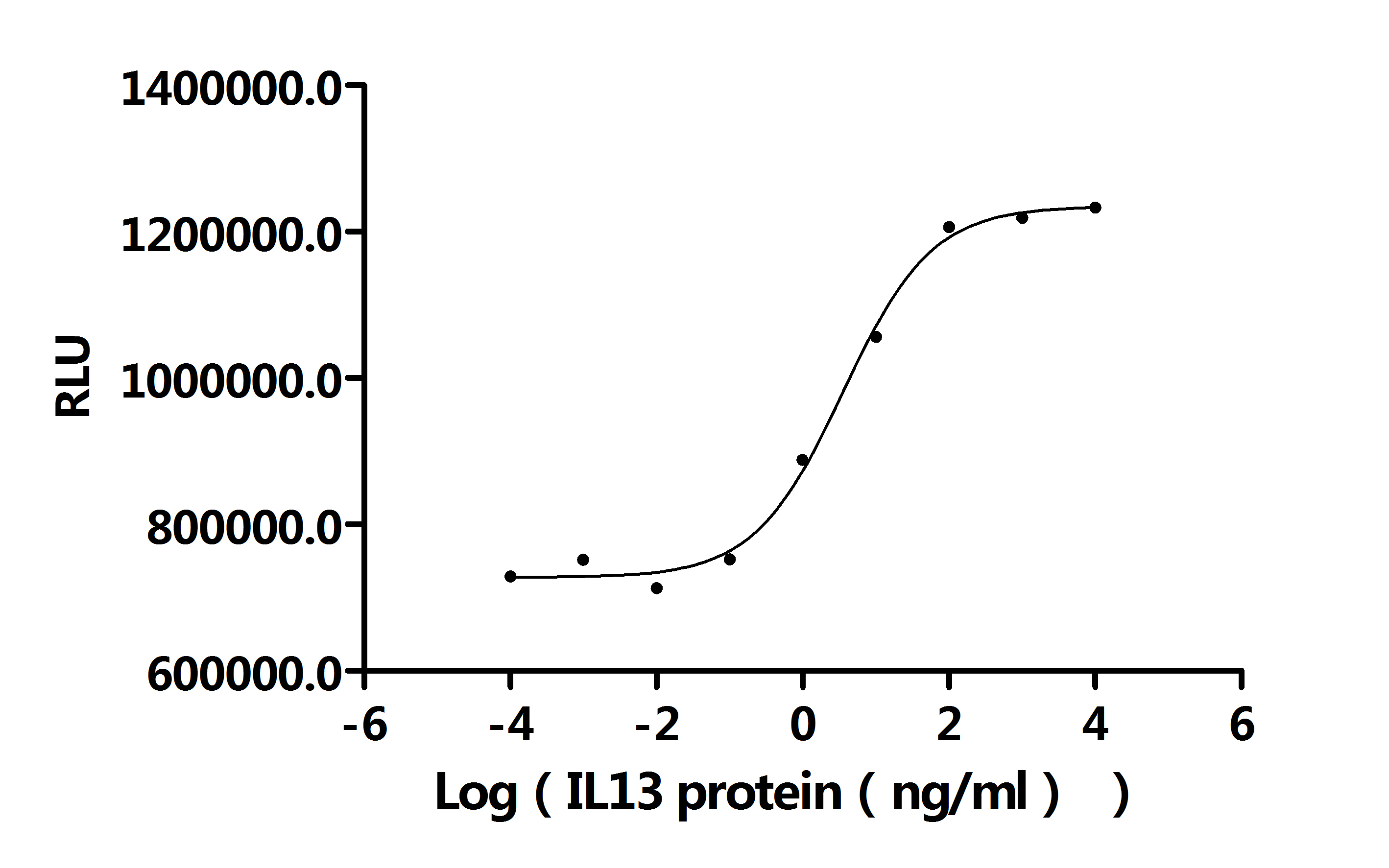
- IL13: IL13 plays a key role in multiple autoimmune and allergic rare diseases. Monoclonal antibody drugs targeting IL13 have been approved for the treatment of asthma and are also under investigation for rare diseases such as eosinophilic esophagitis. Some drugs are in the clinical trial stage, blocking the IL13 signaling pathway to reduce inflammatory responses and improve patient symptoms, offering new treatment hopes for related rare disease patients.
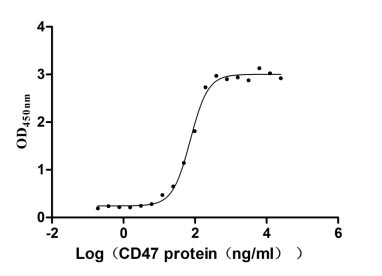
- CD47: CD47 is abnormally expressed in multiple hematological rare diseases and solid tumors. Its binding with signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) can send a "don't eat me" signal, helping tumor cells evade phagocytosis by macrophages. Drug research and development targeting the CD47 receptor mainly focuses on developing antibodies or small molecule inhibitors that block the interaction between CD47 and SIRPα. In the field of rare diseases, some drugs have shown certain therapeutic potential in clinical trials for hematological diseases such as myelodysplastic syndromes.
- SEMA4D: SEMA4D is involved in cell-to-cell communication, immune regulation, and angiogenesis. In rare disease drug research and development, studies targeting the SEMA4D receptor mainly focus on autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. Currently, it is in the preclinical research stage, exploring the possibility of improving disease progression by regulating SEMA4D signaling.
- BTLA: As an important immune regulatory molecule, BTLA has potential therapeutic target value in autoimmune diseases and immune deficiency diseases. Currently, drug research and development targeting BTLA is in the early stage, mainly focusing on studying its role in the immune regulatory network and developing biological agents or small molecule compounds that can regulate BTLA activity, laying the foundation for subsequent clinical trials.
6. Rare Disease Drug Research - Related Products
6.1 Target Proteins
| Target |
Product Name |
Source |
Tag Info |
Product Code |
| ACVR2A |
Recombinant Human Activin receptor type-2A (ACVR2A), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP001260HU1 |
| ACVR2A |
Recombinant Mouse Activin receptor type-2A (Acvr2a), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP001260MO1 |
| ACVR2B |
Recombinant Human Activin receptor type-2B (ACVR2B), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP623829HU |
| ACVR2B |
Recombinant Mouse Activin receptor type-2B (Acvr2b), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP001261MO1 |
| ACVRL1 |
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active) |
Baculovirus |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-BP001262HU1 |
| ANGPT2 |
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP001707HU(A4) |
| ANGPT2 |
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP001707DO |
| BSG |
Recombinant Human Basigin (BSG), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-tagged |
CSB-MP002831HU1 |
| BTLA |
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-Myc-tagged |
CSB-MP773799HU |
| BTLA |
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP773799HU1 |
| C5AR1 |
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged (This tag can be tested only under denaturing conditions) |
CSB-MP003996HU |
| CCN2 |
Recombinant Macaca mulatta CCN family member 2 (CCN2) (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP5112MOW |
| CCR4 |
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CCR4) (Active) |
in vitro E.coli expression system |
N-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-CF004843HU |
| CCR4 |
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CCR4)-VLPs (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged (This tag can be tested only under denaturing conditions) |
CSB-MP004843HU |
| CCR8 |
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged (This tag can be tested only under denaturing conditions) |
CSB-MP004847HU |
| CD22 |
Recombinant Human B-cell receptor CD22 (CD22), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP004900HU |
| CD274 |
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-tagged |
CSB-MP878942HU1 |
| CD276 |
Recombinant Human CD276 antigen (CD276), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal hFc-Myc-tagged |
CSB-MP733578HU |
| CD276 |
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD276 molecule(CD276), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP5140MOV |
| CD276 |
Recombinant Human CD276 antigen (CD276), partial (Active) |
Mammalian cell |
C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
CSB-MP733578HU(F2) |
6.2 Recombinant Antibodies
| Target Name |
Product Name |
Species Reactivity |
Tested Applications |
Code |
| ACVR2B |
ACVR2B Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA260702A0HU |
| ACVR2B |
ACVR2B Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC, IF |
CSB-RA623829MA1HU |
| ACVRL1 |
ACVRL1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-RA555022A0HU |
| ACVRL1 |
ACVRL1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-RA001262MA1HU |
| ANGPT2 |
ANGPT2 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA191985A0HU |
| ANGPT2 |
ANGPT2 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-RA001707MA01HU |
| AOC3 |
AOC3 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA624122MA1HU |
| APC |
APC Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
CSB-RA951649A0HU |
| APCS |
APCS Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA001898MA1HU |
| APP |
APP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IF |
CSB-RA994273A0HU |
| APP |
APP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC, IF |
CSB-RA001950MA2HU |
| APP |
APP Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IF, FC |
CSB-RA001950MA3HU |
| AQP4 |
AQP4 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA548145A0HU |
| BTLA |
BTLA Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, FC |
CSB-RA773799MA1HU |
| C1S |
C1S Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA003657MA1HU |
| C5 |
C5 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, FC |
CSB-RA003995MA1HU |
| C5AR1 |
C5AR1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA |
CSB-RA003996A0HU |
| CA9 |
CA9 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA614990A0HU |
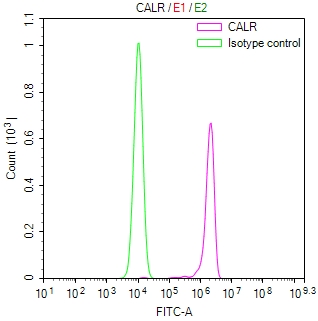
| CALR |
CALR Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC |
CSB-RA004458MA1HU |
| CCL2 |
CCL2 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
CSB-RA004783MA1HU |
6.3 ELISA Kits
| Target |
Product Name |
Sample Types |
Detection Range |
Code |
| ADAMTS13 |
Human von Willebrand Factor cleaving protease,ADAMTS-13/vWF-cp ELISA Kit |
|
|
CSB-E13487h |
| ADAMTS13 |
Mouse ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13 (ADAMTS13) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
78 pg/mL-5000 pg/mL |
CSB-EL001301MO |
| ADM |
Dog adrenomedullin,ADM ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell culture supernates |
15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL |
CSB-E09836c |
| ADM |
Human adrenomedullin,ADM ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.312 pg/mL-20 pg/mL |
CSB-E09146h |
| ADM |
Mouse adrenomedullin,ADM ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates |
4.7 pg/mL-300 pg/mL |
CSB-E10061m |
| ANGPT2 |
Human Angiopoietin 2,ANG-2 ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
39 pg/mL-2500 pg/mL |
CSB-E04500h |
| ANGPT2 |
Rat Angiopoietin 2,ANG-2 ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates. |
0.02 ng/ml-50 ng/ml. |
CSB-E07304r |
| ANGPT2 |
Mouse Angiopoietin 2,ANG-2 ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates |
0.156 pg/mL-10 pg/mL |
CSB-E07305m |
| ANGPT2 |
Pig Angiopoietin 2,ANG-2 ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
0.94 ng/mL-60 ng/mL |
CSB-E08460p |
| ANGPTL3 |
Human angiopoietin-like protein 3,ANGPTL3 ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
78 pg/mL-5000 pg/mL |
CSB-E11724h |
| ANGPTL3 |
Mouse Angiopoietin-related protein 3(ANGPTL3) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
31.25 pg/mL-2000 pg/mL |
CSB-EL001711MO |
| AOC3 |
Mouse Membrane primary amine oxidase(AOC3) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
1.25 ng/mL-80 ng/mL |
CSB-EL001855MO |
| AOC3 |
Rat Membrane primary amine oxidase(AOC3) ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
7.8 ng/mL-500 ng/mL |
CSB-EL001855RA |
| APC |
Human activated protein C,APC ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
1.56 pg/mL-100 pg/mL |
CSB-E09909h |
| APC |
Mouse activated protein C,APC ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
62.5 pg/mL-4000 pg/mL |
CSB-E09914m |
| APC |
Pig activated protein C(APC) ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
40 pg/mL-8000 pg/mL |
CSB-E12633p |
| APCS |
Human Serum amyloid P,SAP ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
7.8 ng/mL-500 ng/mL |
CSB-E09958h |
| APLN |
Human Apelin ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, cell culture supernates |
125 pg/mL-8000 pg/mL |
CSB-E14334h |
| APLN |
Mouse Apelin ELISA kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
31.25 pg/mL-2000 pg/mL |
CSB-E12027m |
| APOH |
Mouse apolipoprotein H (Apo-H) ELISA Kit |
serum, plasma, tissue homogenates |
15.6 ng/mL-1000 ng/mL |
CSB-E10074m |


-AC1.jpg)