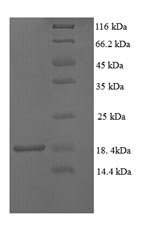
The target gene is synthesized by fusing the 6xHis tag gene to the N-terminus of the gene fragment that codes for the mature human TTR antigen covering amino acids 21-147. This target gene undergoes PCR amplification and is cloned into expression vectors to create recombinant plasmids. The plasmids are then introduced into E. coli cells, which are cultured to enable protein expression. The supernatant is collected and purified through affinity chromatography, producing recombinant human TTR protein with a purity level above 90%, as demonstrated by SDS-PAGE.
Macaca fascicularis is a non-human primate species widely utilized in biomedical research due to its physiological and genetic similarities to humans. One notable area of research involves transthyretin (TTR), a protein that plays a crucial role in the transport of thyroid hormones and retinol-binding protein in the bloodstream.
TTR is particularly significant in the context of amyloidosis. Studies have shown that TTR can misfold and aggregate, resulting in amyloid fibril formation, which is implicated in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) [1]. The Macaca fascicularis serves as a valuable model for studying this condition, as it shares similar physiological responses to TTR-related diseases as humans [1].
Research involving Macaca fascicularis has demonstrated the expression and localization of TTR in various tissues, contributing to a better understanding of its role in health and disease. For instance, while the expression of TTR in peripheral blood mononuclear cells has been studied, the specific regulatory functions during different physiological states require further investigation [2]. Furthermore, the genetic makeup of Macaca fascicularis has been sequenced, providing insights into the TTR gene and its variants, which can influence susceptibility to amyloid diseases [3].
References:
[1] K. Murakami, N. Izuo, & G. Bitan, Aptamers targeting amyloidogenic proteins and their emerging role in neurodegenerative diseases, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 298, no. 1, p. 101478, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101478
[2] J. Xu, Y. Xu, B. Miao, M. Deng, Y. Wang, P. Xiang, et al., Influence of menstrual cycle on the expression of clock genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in macaca fascicularis, European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology, vol. 186, p. 54-58, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2015.01.003
[3] T. Tan, L. Xia, K. Tu, J. Tang, S. Yin, L. Dai, et al., Improved macaca fascicularis gene annotation reveals evolution of gene expression profiles in multiple tissues, BMC Genomics, vol. 19, no. 1, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5183-y