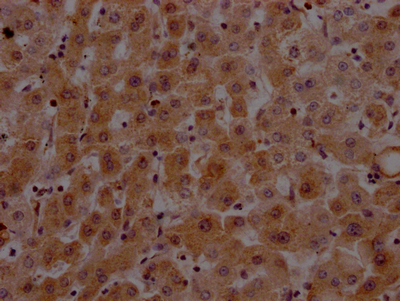
The F2 recombinant monoclonal antibody can detect human F2 protein in ELISA and IHC applications. It is produced using recombinant DNA technology, wherein the gene coding for the F2 monoclonal antibody is synthesized by sequencing the cDNA of the F2 antibody-producing hybridomas. The hybridomas are generated by fusing myeloma cells with B cells that were isolated from an animal immunized with a synthesized peptide derived from human prothrombin. The synthesized gene is then inserted into a vector and transfected into cells for cultivation. The resulting F2 recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified from the cell culture supernatant through affinity chromatography.
Coagulation factor II (F2), also known as prothrombin, is a protein that plays an essential role in the blood clotting process. In response to injury, prothrombin is converted to thrombin, an enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin forms a mesh-like network that stabilizes the blood clot and stops bleeding. The activation of prothrombin to thrombin is a critical step in the coagulation cascade and requires the presence of other factors and cofactors.