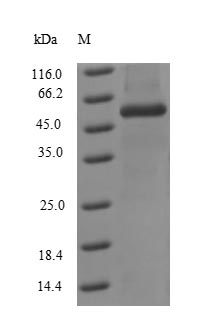
Recombinant Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein (NP) is produced in E. coli and includes the full-length sequence from 1 to 498 amino acids, ensuring complete representation of the native protein. It features an N-terminal 6xHis-tag for convenient purification and detection. The protein appears to be highly purified, with a purity exceeding 90% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis, making it suitable for various research applications requiring high-quality protein.
The Nucleoprotein (NP) of the Influenza A virus plays a crucial role in the virus's life cycle, particularly in RNA genome replication and packaging. It's a vital component of the ribonucleoprotein complex and is involved in the nuclear import of viral RNA. Because of its essential function in viral replication, NP has become a significant focus in influenza research, providing insights into viral assembly and potential antiviral targets.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Influenza A virus nucleoprotein is a viral RNA-binding protein that requires precise folding, proper oligomerization, and specific RNA-binding activity for its functional role in viral replication. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic folding environment or post-translational modifications that may be important for native NP structure. While the full-length protein (1-498aa) contains all functional domains, the N-terminal 6xHis-tag may sterically interfere with the protein's oligomerization interfaces or RNA-binding domains. The probability of correct folding with functional RNA-binding and oligomerization activity requires experimental validation.
1. Antibody Development and Validation Studies
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional protein folding. The full-length protein provides comprehensive epitope coverage for generating antibodies against influenza NP. The high purity (>90%) ensures minimal contamination-related issues during immunization protocols.
2. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This application carries a significant risk without proper folding validation. NP interactions with viral polymerase components and host factors require precise oligomerization and tertiary structure. If correctly folded (verified), the protein may identify physiological interaction partners. If misfolded/unverified, there is a high risk of non-specific binding or failure to replicate genuine viral complex formation.
3. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
These studies are essential for determining folding status. Techniques should include size-exclusion chromatography to assess oligomeric state, circular dichroism spectroscopy to evaluate secondary structure, and RNA-binding assays to validate functionality. However, the His-tag may interfere with crystallization for high-resolution structural studies.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli-expressed influenza NP with N-terminal His-tag is suitable for antibody development and structural characterization, but has limitations for functional and vaccine applications. Begin with Application 3 (Structural Characterization) to assess oligomerization state through SEC and validate RNA-binding capability. Applications 1 (antibody development) can proceed immediately. For Application 2 (interaction studies), first confirm proper folding and oligomerization. Avoid vaccine research due to potential conformational differences from native viral NP. For vaccine development, consider using mammalian-expressed NP or virus-derived protein to ensure proper conformational epitopes.