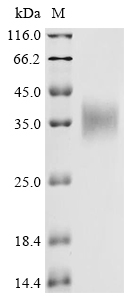
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Erythropoietin (EPO) is produced in a mammalian cell expression system, which appears to ensure appropriate post-translational modifications. The protein corresponds to the full-length mature sequence and includes an N-terminal 6xHis-Myc tag for ease of purification and detection. With a purity greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE, this product seems suitable for research applications requiring high-quality recombinant proteins.
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a vital glycoprotein hormone primarily responsible for regulating red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) in the bone marrow. It plays an essential role in maintaining the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood and serves as a key factor in response to hypoxia. EPO is also involved in various signaling pathways and has become a significant focus in hematology and regenerative medicine research.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Macaca fascicularis EPO is a complex glycoprotein hormone that requires precise folding, proper disulfide bond formation, and specific glycosylation patterns for its functional activity in erythropoiesis. The mammalian cell expression system provides the necessary eukaryotic environment for correct folding, disulfide bonding, and relevant glycosylation. However, the N-terminal 6xHis-Myc tag may sterically interfere with the protein's receptor-binding domains and functional conformation. While the full-length mature protein (28-192aa) contains all functional domains, the probability of correct folding with full bioactivity requires experimental validation due to potential tag interference.
1. Comparative Protein Structure and Function Studies
This application carries a significant risk without functional validation. EPO's structural and functional comparisons require native conformation and proper receptor-binding capability. If correctly folded and active (verified through receptor binding assays), the protein may enable valid comparative studies. If the tag interferes with folding/function (unverified), comparative analyses would yield misleading evolutionary and functional insights.
2. Antibody Development and Cross-Reactivity Testing
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition. The mammalian-expressed EPO provides proper folding and relevant glycosylation, making it an excellent immunogen. However, antibodies may primarily target the tags or may not recognize conformational epitopes if the tag alters protein structure.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This application carries a high risk. EPO interactions with its receptor require precise tertiary structure. The tags may sterically hinder binding sites or create artificial interaction surfaces. If misfolded/unverified, pull-down assays may yield non-specific or tag-mediated artefacts rather than genuine physiological interactions.
4. In Vitro Assay Development and Validation
This application requires functional validation. Cell-based EPO assays depend on native receptor binding and signaling capability. If the tag compromises bioactivity (unverified), assay results will be biologically misleading. Dose-response studies may not reflect true potency if tagging reduces activity.
5. Immunogenicity and Safety Assessment Studies
This application carries significant limitations. The tags themselves are immunogenic and may dominate the immune response, making it difficult to assess EPO-specific immunogenicity. Results may not accurately predict the immunogenicity of native, tag-free EPO in clinical settings.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The mammalian-expressed EPO with N-terminal tags has a high probability of proper folding due to the appropriate expression system, but the tags may compromise bioactivity by interfering with receptor-binding domains. Begin with functional validation using receptor binding assays and cell-based proliferation tests before considering any functional applications. Application 2 (antibody development) can proceed with awareness of potential tag dominance. Applications 1, 3, and 4 require rigorous bioactivity validation. Application 5 has limited predictive value for native EPO immunogenicity. For reliable EPO research requiring native functionality, use tag-free EPO expressed in mammalian systems.