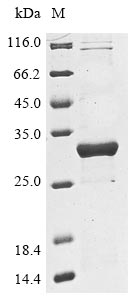
Recombinant Klebsiella pneumoniae Beta-lactamase SHV-3 is produced in E. coli and includes the complete mature protein sequence spanning amino acids 22 to 286. The protein carries an N-terminal 6xHis-tag, which simplifies both purification and detection processes. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms protein purity above 85%. This research-only product appears well-suited for controlled applications, with endotoxin levels kept under tight management to support consistent experimental outcomes.
Beta-lactamase SHV-3 represents a key enzyme in bacterial defense against beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins and cephalosporins. The enzyme works by breaking down the beta-lactam ring structure, essentially neutralizing the antibiotic's effectiveness. Research into this protein may reveal important details about how antibiotic resistance develops, potentially guiding the creation of new treatment approaches and advancing our understanding of bacterial survival mechanisms and resistance pathways.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Because SHV-3 is a periplasmic enzyme in its native host, expressing it in E. coli (a closely related Gram-negative system) is generally compatible with proper protein folding and disulfide bond formation—especially if directed to the periplasm or expressed as a soluble form. The active site architecture and metal-ion dependence (none required) of SHV-type beta-lactamases are straightforwardly maintained under bacterial expression. Therefore, the recombinant protein very likely retains its native fold and enzymatic activity, provided that expression was soluble (not inclusion bodies). However, bioactivity cannot be assumed without experimental confirmation (e.g., activity assay).
1. Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism Studies
This recombinant SHV-3 beta-lactamase can be used to explore antibiotic resistance mechanisms in K. pneumoniae. If enzymatic activity is confirmed, it can be used in in vitro kinetic assays to determine substrate specificity, catalytic efficiency, and inhibition constants across beta-lactam classes. If enzymatic activity has not been verified, it can still serve as a qualitative reagent for structural modeling or testing assay conditions before working with active preparations. The His-tag facilitates purification and immobilization for repeated kinetic measurements and biophysical characterization.
2. Inhibitor Screening and Development
If the enzyme is enzymatically active, this recombinant SHV-3 is an excellent tool for screening beta-lactamase inhibitors using colorimetric, fluorometric, or ELISA-based methods. If the activity is unverified or lost during expression, it may still serve for preliminary binding or surface interaction screening, but not for functional inhibitor testing. The N-terminal His-tag enables immobilization on nickel-coated assay plates for reproducible high-throughput screening assays.
3. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
This recombinant SHV-3 is well-suited for structural biology and stability studies, particularly if expressed in soluble, folded form. Properly folded SHV-3 can be subjected to X-ray crystallography, NMR, or cryo-EM to resolve its tertiary structure and compare it with other beta-lactamase variants. If the protein proves partially unfolded, it remains useful for refolding studies, secondary structure analysis (CD spectroscopy), and thermal stability assessments, offering insight into structural robustness and folding intermediates. The >85% purity supports these downstream applications.
4. Antibody Development and Immunoassay Applications
The recombinant protein is highly suitable as an immunogen for generating antibodies against SHV-3. If folded correctly, antibodies raised against it will recognize both native and denatured forms of SHV-3. If misfolded, the protein still serves effectively for polyclonal antibody production or linear epitope detection in ELISA and Western blot assays. The His-tag also enables immobilization and purification during antibody validation steps.
5. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This application is partially correct but should be refined. While SHV-3 primarily functions as a hydrolytic enzyme rather than a protein-interacting regulatory component, it may still participate in limited protein-protein interactions, such as with periplasmic chaperones, membrane anchors, or beta-lactamase inhibitor proteins (BLIPs). If the recombinant enzyme is folded correctly, it can be used in pull-down or SPR/BLI assays to investigate such interactions. If not folded properly, interaction studies would be non-physiological and should instead focus on epitope mapping or refolding optimization.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The recombinant SHV-3 beta-lactamase (22–286aa) expressed in E. coli likely retains its native conformation and catalytic activity, making it a strong candidate for mechanistic enzymology, inhibitor screening, and structural analysis. However, as enzymatic activity has not been explicitly validated, all downstream applications should proceed under two assumptions—active versus inactive forms—until confirmed experimentally. If activity is confirmed, prioritize kinetic and inhibition studies. If inactive, focus on antibody development, refolding trials, or structural characterization of inactive intermediates.