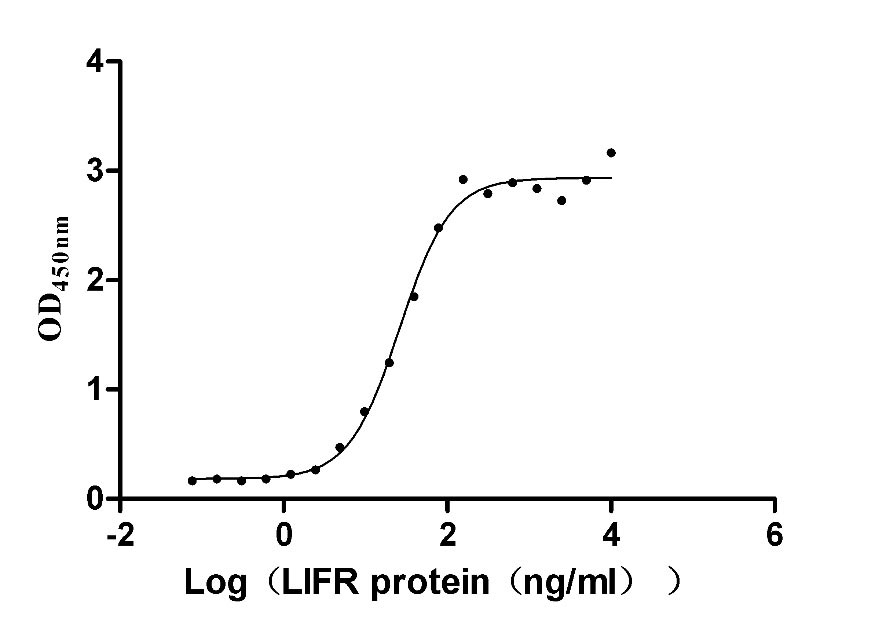
The recombinant human LIF protein is produced in mammalian cells. Its expression region corresponds to the 23-202aa of the human LIF protein. It is tagged with a C-terminal hFc tag for easy detection and purification. The LIF protein has a purity of over 90%, as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, and contains less than 1.0 EU/µg endotoxin, as determined by the LAL method. Its biological activity is measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA, where immobilized human LIF at 2 μg/ml can bind to human LIFR (CSB-MP012929HUi9) with an EC50 range of 22.58-30.24 ng/ml.
LIF is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the IL-6 family, which plays critical roles in various biological processes, including hematopoiesis, embryonic development, and immune responses. LIF is primarily known for its involvement in the maintenance of stem cell pluripotency and differentiation, particularly in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) [1][2]. The signaling pathway activated by LIF involves the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), which, upon binding with LIF, activates several intracellular signaling cascades, including the JAK-STAT pathway, particularly STAT3 [3][4]. This activation is crucial for promoting the expression of genes that maintain the undifferentiated state of stem cells while inhibiting differentiation [1][2].
LIF plays a role in immune modulation. It has been shown to influence the differentiation of myeloid cells, such as the murine M1 myeloid leukemia cell line, into macrophages [5][6]. LIF can alter the phenotype of T cells and macrophages from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state, which is particularly relevant in the context of neuroprotection and inflammation [4]. This ability to modulate immune responses suggests that LIF could be a potential therapeutic target in conditions characterized by inflammation or immune dysregulation.
LIF is also implicated in reproductive biology, particularly in embryo implantation. It has been identified as a key factor in uterine receptivity, facilitating the implantation of the embryo by modulating the local immune environment and promoting the necessary physiological changes in the endometrium [7][8]. The presence of LIF is critical for successful implantation, and its absence can lead to reproductive challenges. Moreover, LIF's role extends to the regulation of metabolic processes, where it has been shown to influence energy homeostasis and body weight regulation. Studies have indicated that LIF expression in the hypothalamus is associated with the regulation of energy intake and obesity, highlighting its potential role in metabolic disorders [9].
References:
[1] B. Youngblood, R. Alfano, S. Pettit, D. Zhang, H. Dallmann, N. Huang, et al. Application of recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor (lif) produced in rice (oryza sativa l.) for maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cells, Journal of Biotechnology, vol. 172, p. 67-72, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.12.012
[2] R. Alfano, B. Youngblood, D. Zhang, N. Huang, & C. MacDonald. Human leukemia inhibitory factor produced by the expresstec method from rice (oryza satival.) is active in human neural stem cells and mouse induced pluripotent stem cells, Bioengineered, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 180-185, 2014. https://doi.org/10.4161/bioe.28996
[3] A. Catunda, E. Gócza, B. Carstea, L. Hiripi, H. Hayes, C. Rogel-Gaillard, et al. Characterization, chromosomal assignment, and role of lifr in early embryogenesis and stem cell establishment of rabbits, Cloning and Stem Cells, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 523-534, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1089/clo.2008.0023
[4] S. Davis and K. Pennypacker. The role of the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor in neuroprotective signaling, Pharmacology & Therapeutics, vol. 183, p. 50-57, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.08.008
[5] X. Wang, H. Wu, Z. Zhang, S. Liu, J. Yang, X. Chen, et al. Effects of interleukin-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and ciliary neurotrophic factor on the proliferation and differentiation of adult human myoblasts, Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, vol. 28, no. 1, p. 113-124, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-007-9247-9
[6] E. Kim, H. Choi, T. Chung, S. Jang, K. Kim, & K. Ha. Expression and efficient one-step chromatographic purification of a soluble antagonist for human leukemia inhibitory factor receptor in escherichia coli, Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, vol. 25, no. 8, p. 1307-1314, 2015. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1501.01094
[7] L. Aghajanova. Leukemia inhibitory factor and human embryo implantation, Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, vol. 1034, no. 1, p. 176-183, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1335.020
[8] R. Kanegi, S. Hatoya, Y. Tsujimoto, S. Takenaka, T. Nishimura, V. Wijewardana, et al. Production of feline leukemia inhibitory factor with biological activity in escherichia coli, Theriogenology, vol. 86, no. 2, p. 604-611, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.02.013
[9] M. Fioravante, B. Bombassaro, A. Ramalho, N. Dragano, J. Morari, C. Solon, et al. Inhibition of hypothalamic leukemia inhibitory factor exacerbates diet-induced obesity phenotype, Journal of Neuroinflammation, vol. 14, no. 1, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0956-9