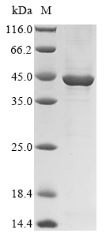
Recombinant Chlamydia trachomatis Major outer membrane porin, serovar D (ompA) gets produced in E. coli and spans the complete mature protein sequence from amino acids 23 to 393. The protein comes with an N-terminal 10xHis-tag and a C-terminal Myc-tag, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms it reaches greater than 90% purity - a level that appears suitable for research applications where high purity matters.
The Major outer membrane porin (ompA) of Chlamydia trachomatis represents a key element of the bacterial outer membrane. It likely plays an important role in keeping membrane integrity and structure intact. This protein forms a porin that allows small molecules and ions to pass through, and seems essential for the pathogen to survive. Researchers find it valuable because it's involved in studies examining how bacteria cause disease and how pathogens interact with their hosts.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Based on the provided information, the folding state and bioactivity of this recombinant OmpA protein are unknown and must be considered unverified. OmpA is a major outer membrane protein that typically forms beta-barrel structures and functions as a porin. Correct integration into a membrane is often crucial for its proper folding and function. Expression in the cytoplasm of E. coli, without the specific machinery for outer membrane protein insertion, makes it highly uncertain whether this recombinant version has adopted its correct, native tertiary structure. The presence of tags on both termini further complicates correct folding. Therefore, any application that depends on the protein's native conformation or porin activity is speculative without experimental validation.
1. Immunological Studies and Antibody Development
This recombinant OmpA protein is suitable for use as an immunogen to generate polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies. Both the His and Myc tags facilitate purification and detection during antibody production and screening. The >90% purity is appropriate for immunization protocols. However, it is critical to note that the antibodies generated will be against the linear sequence and the recombinant form of the protein. Their ability to recognize the natively folded, membrane-embedded OmpA protein in C. trachomatis elementary bodies must be empirically confirmed, as the epitopes may be different.
2. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The dual tags make this protein practical for pull-down or co-immunoprecipitation experiments to identify potential binding partners. However, a fundamental caveat is that the utility of these assays is entirely dependent on the recombinant protein being correctly folded. If the protein is misfolded, it may not present the correct interaction surfaces. Any interactions identified could be non-specific or irrelevant to its native function, while a negative result could be due to misfolding.
3. ELISA-Based Binding Assays
The dual-tagged recombinant OmpA can be used in ELISA formats. However, the applicability of these assays depends entirely on the goal. It is well-suited for studying antibody interactions (as in Application 1). In contrast, using it to study "binding with host cell receptors" is highly speculative and contingent upon correct folding. The tags provide standardized methods, but they do not ensure that the receptor-binding domains of OmpA are functional. Such studies should not be undertaken without first confirming the protein's native structure.
4. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This purified recombinant OmpA protein is well-suited for basic biochemical and biophysical characterization, such as molecular weight confirmation, thermal stability profiling, and aggregation state analysis. This application is valid and is largely independent of the protein's native bioactivity, as it focuses on intrinsic physical properties. The high purity supports accurate measurements for these purposes.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The immediate and critical priority is to attempt to assess the protein's structural state, as its function as a porin is likely compromised due to cytoplasmic expression. Techniques like circular dichroism to check for beta-sheet content (characteristic of the beta-barrel) or limited proteolysis to assess folding compactness should be employed before any functional studies. Applications 1 and 4 are the most feasible starting points, as they do not strictly require native folding. Applications 2 and 3, which rely on specific, native interactions, should be considered highly uncertain and should not be pursued as primary goals without evidence of correct structure. Generating antibodies against this recombinant protein (Application 1) is a valid strategy, but their effectiveness for detecting native OmpA must be tested separately.