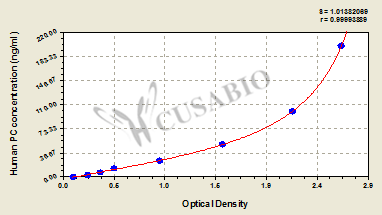
The human protein C (PC) ELISA kit can quantify human protein C in serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates. This kit features a detection range of 3.12 ng/mL to 200 ng/mL and a sensitivity of 0.78 ng/mL. The assay principle is based on a sandwich ELISA method, where the human protein C within a sample is captured between two antibodies for accurate measurement. The assay can be completed within 1 to 5 hours, requiring a sample volume of 50-100 µl. The detection is performed at a wavelength of 450 nm, ensuring precise and reliable results.
Human protein C is a vital component in blood coagulation, being a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein that circulates in plasma as an inactive zymogen. Studies have indicated that blocking the anticoagulant activity of human protein C can improve clotting defects in conditions like hemophilia. Deficiencies in protein C have been associated with congenital thrombotic diseases, underscoring the protein's significance in maintaining proper hemostasis [1].
References:
[1] J. Griffin, B. Evatt, T. Zimmerman, A. Kleiss, & C. Wideman, "Deficiency of protein c in congenital thrombotic disease.", Journal of Clinical Investigation, vol. 68, no. 5, p. 1370-1373, 1981. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci110385