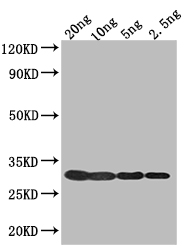
To produce polyclonal antibodies against Enterobacteria phage T7 (Bacteriophage T7) 1 protein (T7 gp1), a rabbit undergoes repetitive immunizations with recombinant Enterobacteria phage T7 (Bacteriophage T7) 1 protein (710-805aa). Upon reaching an optimal antibody titer, the rabbit is bled, and antibodies are purified from the serum using affinity chromatography. The functionality of the resulting T7 gp1 antibody is subsequently evaluated through ELISA and WB applications, demonstrating its ability to interact with Enterobacteria phage T7 (Bacteriophage T7) 1 protein.
The Enterobacteria phage T7 1 protein is a crucial component during the early stages of the phage infection cycle. The T7 gp1 protein interacts with the T7 RNA polymerase, enhancing its specificity for the T7 phage promoters and preventing it from indiscriminately binding to host bacterial DNA. This ensures that the transcriptional machinery is accurately targeted to the phage genes, facilitating the efficient expression of phage genes and enabling the replication of the phage within the host bacterium during the infection process.