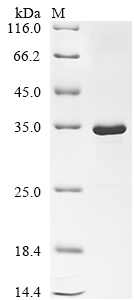
The expression region of this recombinant Escherichia phage T7 (Bacteriophage T7) T7 RNA polymerase covers amino acids 274-509. The expected molecular weight for the T7 RNA polymerase protein is calculated to be 34.6 kDa. This T7 RNA polymerase recombinant protein is manufactured in e.coli. The T7 RNA polymerase coding gene included the N-terminal 10xHis tag and C-terminal Myc tag, which simplifies the detection and purification processes of the recombinant T7 RNA polymerase protein in following stages of expression and purification.
The Escherichia phage T7 RNA polymerase (T7 RNAP) is an enzyme encoded by the T7 bacteriophage genome. It is a single-subunit RNA polymerase that recognizes and transcribes genes under the control of T7 promoter sequences. T7 RNAP is highly specific and efficient, making it a valuable tool in molecular biology research, particularly for in vitro transcription of RNA. Its use is prevalent in various applications, such as synthesizing RNA probes, producing RNA for structural studies, and generating messenger RNA (mRNA) for recombinant protein expression. T7 RNAP has become a standard component in molecular biology laboratories for its robustness and utility in diverse experimental techniques.