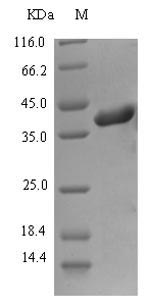
Recombinant Epstein-Barr virus Envelope glycoprotein H (gH) is produced in E. coli with an expression region spanning amino acids 19 to 218. This partial protein carries an N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag for improved solubility and purification. The product reaches purity levels above 90%, as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, which appears to make it suitable for various experimental applications. This protein is intended for research use only.
Epstein-Barr virus Envelope glycoprotein H (gH) represents a crucial component of the viral envelope. It plays what seems to be a significant role in the fusion process during viral entry into host cells. The protein interacts with other glycoproteins to enable membrane fusion—a process that's essential for viral infection. Understanding gH function and structure may prove important in virology research, particularly for studies examining viral entry mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Epstein-Barr virus Envelope glycoprotein H (gH) is a complex viral glycoprotein that requires precise folding, proper glycosylation at multiple sites, correct disulfide bond formation, and specific tertiary structure for its functional activity in viral entry and membrane fusion. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the eukaryotic folding environment, glycosylation machinery, or optimal conditions for disulfide bond formation. The large N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag (∼15 kDa) may sterically interfere with the protein's folding and functional domains, especially since the partial fragment (19-218aa, ∼22 kDa) is similar in size to the tag. The probability of correct folding with bioactivity is extremely low without experimental validation.
1. Antibody Development and Characterization
This application has significant limitations. Antibody development may generate responses against linear epitopes, but the non-glycosylated, potentially misfolded protein will not present conformational epitopes found on the native glycoprotein. Antibodies may primarily target the foreign tags or non-physiological structures, reducing their utility for detecting native gH in viral contexts.
2. Structural and Biochemical Characterization
Basic biophysical analysis can be performed, but will not reflect native gH structure. Techniques like circular dichroism spectroscopy or dynamic light scattering can assess the recombinant fragment's properties, but the lack of glycosylation and potential improper folding mean results describe an artificial construct rather than the viral glycoprotein.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed gH fragment is unsuitable for functional studies due to the essential requirements for glycosylation and proper folding that cannot be met in this system. Interaction studies and functional studies should be avoided entirely due to the high risk of artefacts. Application 1 (antibody development) has severe limitations and may produce antibodies with poor recognition of native gH. Application 2 (structural characterization) provides only basic insights into the recombinant fragment. For reliable gH research, use a full-length, glycosylated protein expressed in mammalian or insect cell systems, and validate folding with glycosylation analysis and functional assays.