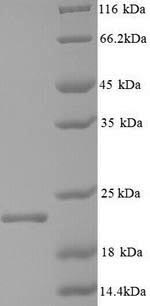
CUSABIO transfected the expression vector which inserted the recombinant DNA into the yeast, cultured the cells, and then induced the transcription and translation of the cloned vector. The N-terminal 6xHis tag sequence was appended to the gene coding for the yeast of the HBV-C Capsid protein (C) protein to form the recombinant DNA. The recombinant HBV-C Capsid protein (C) was expressed as N-terminal 6xHis-tagged fusion. The purity of the protein is greater than 90% assayed by SDS-PAGE. It has an apparent molecular weight of approximately 22 kDa.
Hepatitis B virus is an important human pathogen. HBV encodes a 21 kDa core protein, which is required for reverse transcription. This core protein can assemble into stable icosahedral particles, when the electrostatic interactions between positively and negatively charged macromolecules at the inner surface of the capsid shell are adequately balanced. It remains unclear what determines the subcellular localization of hepatitis B virus (HBV) core protein (HBc) and particles. Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus HBV could lead to cirrhosis and highly malignant liver cancer. At present, treatment of hepatitis B is not very effective, due to notorious side effects and drug resistance. The virus can synthesize a core protein for its own replication. Clinically, this core protein tends to be more localized to the cytoplasm when patients' disease is severe, and more localized to the nucleus when the disease is mild.