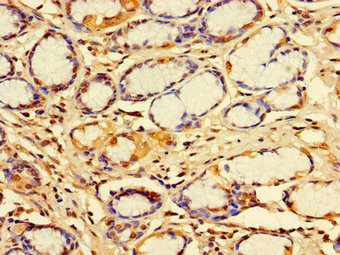
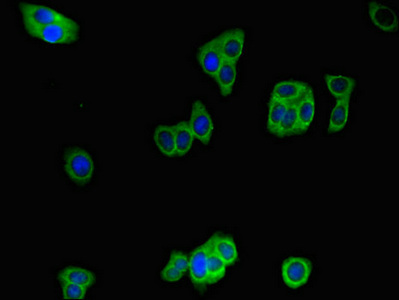
Plays a role in the cellular breakdown of insulin, APP peptides, IAPP peptides, natriuretic peptides, glucagon, bradykinin, kallidin, and other peptides, and thereby plays a role in intercellular peptide signaling. Substrate binding induces important conformation changes, making it possible to bind and degrade larger substrates, such as insulin. Contributes to the regulation of peptide hormone signaling cascades and regulation of blood glucose homeostasis via its role in the degradation of insulin, glucagon and IAPP. Plays a role in the degradation and clearance of APP-derived amyloidogenic peptides that are secreted by neurons and microglia (Probable). Degrades the natriuretic peptides ANP, BNP and CNP, inactivating their ability to raise intracellular cGMP. Also degrades an aberrant frameshifted 40-residue form of NPPA (fsNPPA) which is associated with familial atrial fibrillation in heterozygous patients. Involved in antigen processing. Produces both the N terminus and the C terminus of MAGEA3-derived antigenic peptide (EVDPIGHLY) that is presented to cytotoxic T lymphocytes by MHC class I.; (Microbial infection) The membrane-associated isoform acts as an entry receptor for varicella-zoster virus (VZV).