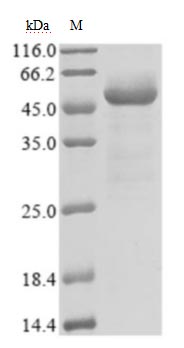
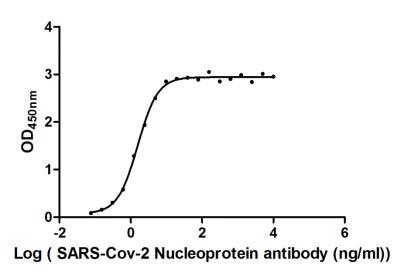
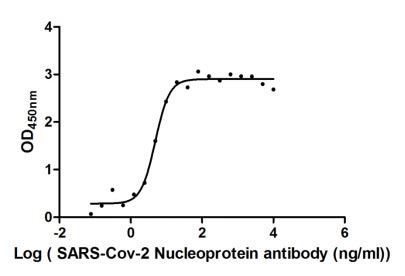
Recombinant severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Nucleoprotein (N) production starts with the isolation of the target gene, incorporating an N-terminal 6xHis-tag to aid in purification. This target gene encoding the1-419aa of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein is inserted into an expression vector, which is subsequently introduced into an E. coli using transformation techniques. The E. coli cell expresses the protein, which accumulates within the cells. The protein is subsequently collected typically through cell lysis and purified using affinity chromatography. Finally, the protein’s activity and functionality are confirmed through functional ELISA tests. It has been demonstrated to be an active protein. Its endotoxin content is less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by the LAL method. Its purity is over 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein (N) is a crucial structural protein of the virus that plays various essential roles in the viral life cycle. It is involved in functions such as replication, packaging, and transcription [1]. The N protein is an RNA-binding protein that forms a helical ribonucleoprotein necessary for SARS-CoV-2's RNA transcription and replication [2]. It is highly conserved and abundantly expressed in SARS-CoV-2, making it a prominent target for diagnostic assays [3]. Studies have shown that the N protein can be detected through seropositivity assays, making it a valuable tool for identifying SARS-CoV-2 infections, including breakthrough infections post-vaccination [4]. Furthermore, the N protein has been utilized in the development of biosensors and immunoassays for antigen detection, highlighting its significance in diagnostic technologies [5][6].
The N protein of SARS-CoV-2 has been the subject of proteomic analysis to understand its interactions with host proteins during infection [7]. It has been identified as a potential target for antiviral therapies, with studies exploring the use of compounds like naproxen that target the N protein to inhibit viral replication [8]. The N protein has also been considered a component of vaccine development due to its immunogenic properties [9].
References:
[1] I. Mahdi, H. Yeasmin, I. Hossain, R. Badhan, A. Ali, M. Kaiumet al., Potential antiviral peptides against the nucleoprotein of sars-cov-2, Chemical Papers, vol. 77, no. 2, p. 813-823, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02514-4
[2] H. Kim, J. Lee, M. Kim, S. Park, M. Choi, W. Leeet al., Development of a sars-cov-2-specific biosensor for antigen detection using scfv-fc fusion proteins, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, vol. 175, p. 112868, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112868
[3] M. Chabi, B. Vu, K. Brosamer, M. Smith, D. Chavan, J. Conradet al., Smartphone-read phage lateral flow assay for point-of-care detection of sars-cov-2 infection,, 2022. https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv-2022-ksshx
[4] L. Hoogen, G. Smits, C. Hagen, D. Wong, E. Vos, M. Bovenet al., Seropositivity to nucleoprotein to detect sars-cov-2 infections: a tool to detect breakthrough infections after covid-19 vaccination,, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.05.21264555
[5] L. Kollhoff, M. Kipping, M. Rauh, U. Ceglarek, G. Barka, F. Barkaet al., Development of a rapid and specific maldi-tof mass spectrometric assay for sars-cov-2 detection,, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.10.23287091
[6] J. Bong, T. Kim, J. Jung, S. Lee, J. Sung, C. Leeet al., Competitive immunoassay of sars-cov-2 using pig sera-derived anti-sars-cov-2 antibodies, Biochip Journal, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 100-108, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00011-6
[7] F. Ciccosanti, M. Rienzo, A. Romagnoli, F. Colavita, G. Refolo, C. Castillettiet al., Proteomic analysis identifies the rna helicase ddx3x as a host target against sars-cov-2 infection, Antiviral Research, vol. 190, p. 105064, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105064
[8] B. Terrier, S. Dilly, M. Pizzorno, J. Henri, F. Berenbaum, B. Linaet al., Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of naproxen: from influenza a to sars-cov-2 coronavirus,, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.30.069922
[9] G. Ahlén, L. Frelin, N. Nikouyan, F. Weber, U. Höglund, O. Larssonet al., The sars-cov-2 n protein is a good component in a vaccine, Journal of Virology, vol. 94, no. 18, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01279-20